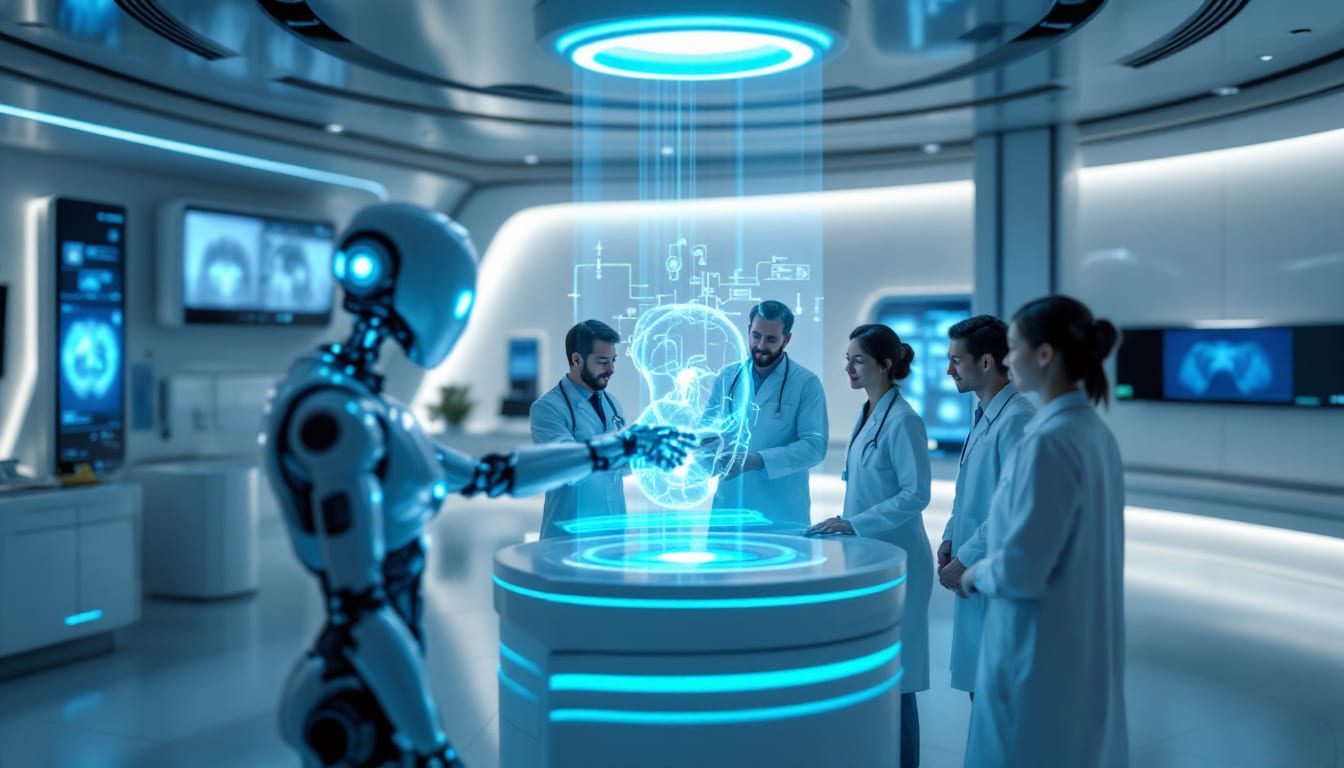
Innovation in medical imaging is experiencing unprecedented growth, as evidenced by recent 510(k) approvals granted to various South Korean companies. Companies such as Neurophet, Vuno And Lunit are now leveraging the capabilities of artificial intelligence to improve disease diagnosis and monitoring, whether through MRI analysis or ECG data. This dynamic highlights the growing importance of technology in the healthcare sector, where each advancement represents significant progress for patient well-being. In addition, French manufacturers are also positioning themselves in this rapidly developing market, highlighting fierce competition and a need for continuous innovation.
Neurophet, a South Korean company specializing in artificial intelligence medical imaging, recently obtained a second 510(k) approval from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its brain image analysis software, Neurophet Aqua. This new functionality allows you to analyze the multiple sclerosis and white matter hyperintensities using T2-FLAIR images.
At the same time, Vuno, a South Korean competitor, has received approval from the South Korean government for its AI-based software capable of analyzing ECG data to identify thehyperkalemia, a condition linked to high levels of potassium in the blood. This software is the third in its range to obtain this approval.
Furthermore, Lunit, also a recognized company in the field of AI medical imaging in South Korea, signed a supply agreement with Salud Digna, one of the largest medical networks in Mexico, to integrate its AI solutions for the analysis of chest x-rays and mammograms.
510(k) approval for South Korean AI Neurophet
South Korean society Neurophet recently obtained a 510(k) authorization for its brain image analysis software, a significant advance for medical imaging. This innovative technology uses artificial intelligence to analyze MRI images of the brain, thus facilitating the detection of neurodegenerative diseases. With this approval, Neurophet Aqua can now analyze T2-FLAIR images, targeting conditions such as multiple sclerosis and the white matter hyperintensities.
the pioneering players in AI in medical imaging
The momentum of artificial intelligence in the medical field is reinforced by companies like Vuno, which recently received approval from the South Korean government for ECG data analysis software. The latter focuses on identifying thehyperkalemia, a dangerous condition caused by elevated potassium levels in the blood. This software represents the third in its series to obtain regulatory approval, attesting to the growing effectiveness of AI in the early detection of health problems.
international collaborations and future prospects
Another company, Lunit, recently signed an agreement with a large medical network in Mexico, involving the application of AI solutions for chest x-rays and the mammography. This collaboration provides Lunit with access to a large database of anonymized medical images, allowing it to adapt its artificial intelligence algorithms to the Latin American market. Innovations in this sector continue to grow, promising future breakthroughs in medical diagnosis.
Recently, we have witnessed significant advances in the field ofmedical imaging, notably with the FDA approval of brain image analysis software developed by the South Korean company Neurophet. This software is designed to analyze magnetic resonance images and has been specifically optimized to identify pathologies such as multiple sclerosis and the white matter hyperintensities. This new feature, which has received the green light under a new 510(k) authorization, demonstrates the technological evolution inartificial intelligence in the medical sector.
This development is part of a broader trend observed in the field ofMedical AI, where many companies, including Vuno, have also marked remarkable progress. Vuno received approval from the South Korean government for its ECG results analysis system, which detectshyperkalemia, a condition that can have serious consequences for health. The positive aspect of these companies highlights the growing importance of AI in improving the accuracy of medical diagnoses.
Here, in France, a windinnovation is also blowing through the medical sector, with an increase in companies obtaining approvals for their AI-based devices. The use of AI for analysis of X-rays and MRIs is becoming a norm, transforming medical practices and increasing doctors’ confidence in these new technologies.
In addition, international collaborations, such as that of Lunit with Mexican networks, enrich the medical landscape by promoting the exchange of data and expertise. These initiatives pave the way for a promising future whereartificial intelligence and the telemedicine will play a central role in improving health care. This dynamic should therefore continue to shape the future of medical imaging globally.