Interventional radiology has undergone a significant transformation thanks to technological advances who revolutionized the methods of guidance and of visualization. The emergence of techniques such assubtraction angiography and the fluoroscopy now makes it possible to optimize interventions, offering real-time images with increased precision. The miniaturization of devices catheterization and the use of devices implantable such as the stents enhance the possibilities for less invasive interventions, while improving the safety and effectiveness of procedures. These innovations open up new perspectives in the medical field, making interventional radiology more accessible and efficient.
There interventional radiology represents a full-fledged discipline of medicine, combining advanced imaging techniques and minimally invasive procedures. It allows the performance of therapeutic interventions while ensuring precise and real-time visualization of anatomical structures. These techniques play an increasingly dominant role in medical practice, particularly in the diagnosis and treatment of vascular, oncological and urological pathologies.
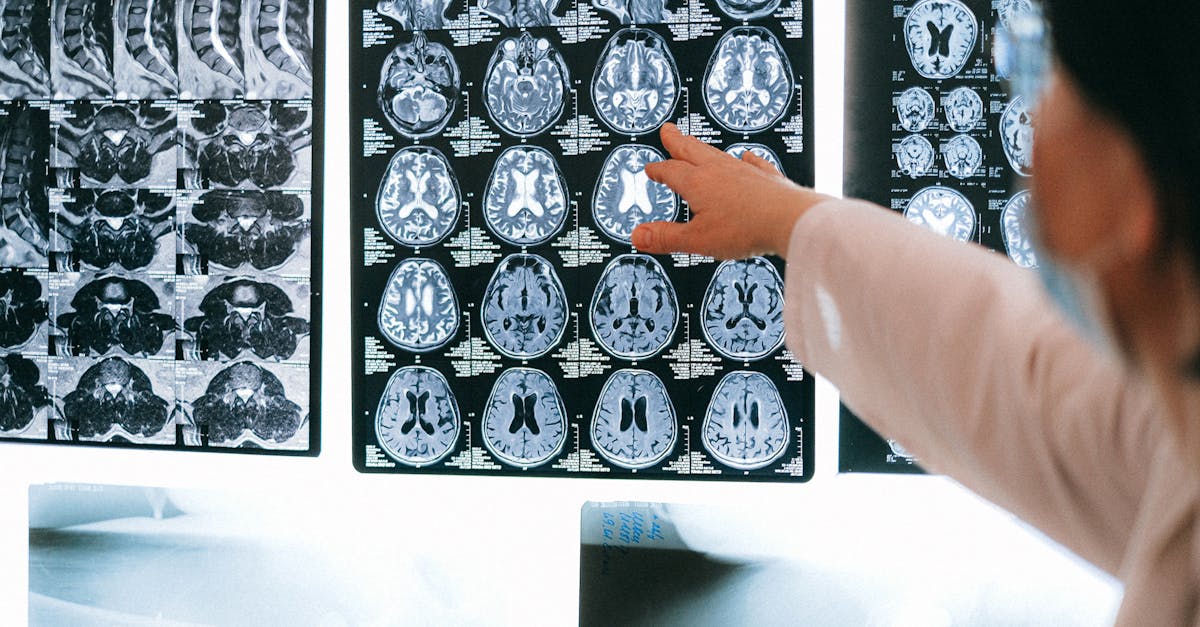
One of the major aspects of the interventional radiology is the use of methods of image guidance. These methods includeultrasound, there fluoroscopy, and theangiography, each having its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the nature of the intervention. Fluoroscopy, for example, uses X-rays to produce continuous images, allowing the doctor to see the path of medical equipment, such as catheters, in real time.
Among recent innovations, technology FORS developed by Philips has revolutionized visualization in interventional imaging. This technology makes it possible to combine several imaging modalities, providing enriched information and facilitating the work of clinicians. This is particularly useful for complex procedures such as embolization, where an embolizer is deployed into a blood vessel to treat malignant lesions or control bleeding.
The miniaturization of tools catheterization is another significant step forward. Intervention instruments, notably microcatheters, make it possible to reach increasingly difficult areas with minimal trauma. This paves the way for less invasive approaches that offer patients faster recovery and fewer post-operative complications.
The development of implantable devices, such as stents, is another area of innovation. The devices can be precisely integrated using advanced imaging techniques, providing benefits in the treatment of obstructive diseases such as stenoses or occlusions. Angioplasty, often performed at the same time as stent placement, is a procedure where a balloon is used to dilate a narrowed artery, which is also guided by imaging.
The minimally invasive nature of the interventional radiology reduces risks for the patient, shortens hospitalization time and convalescence time. Procedures can often be performed on an outpatient basis, easing the burden on the healthcare system and improving the overall patient experience.
The techniques of modern guidance made it possible to improve the precision of the procedures carried out. For example, the stereo-navigation combines preoperative images with real-time data, allowing the doctor to precisely navigate complex anatomical structures. This is particularly relevant in the treatment of tumors or deep lesions where an incorrect approach can have significant consequences.
Within the interventional radiology, different specialties explore various approaches. THE angiographic protocols, for example, play a key role in the treatment of vascular diseases. Embolization and blood vessel diversion techniques are common interventions that rely heavily on imaging for planning and execution.
Another significant technological advance is the introduction of robotization in these procedures. Robot-assisted surgery improves precision and increases control over instrument manipulation by reducing the effects of human hand tremor. The combination of robotics with imaging is particularly used in interventions on the prostate or in oncology.
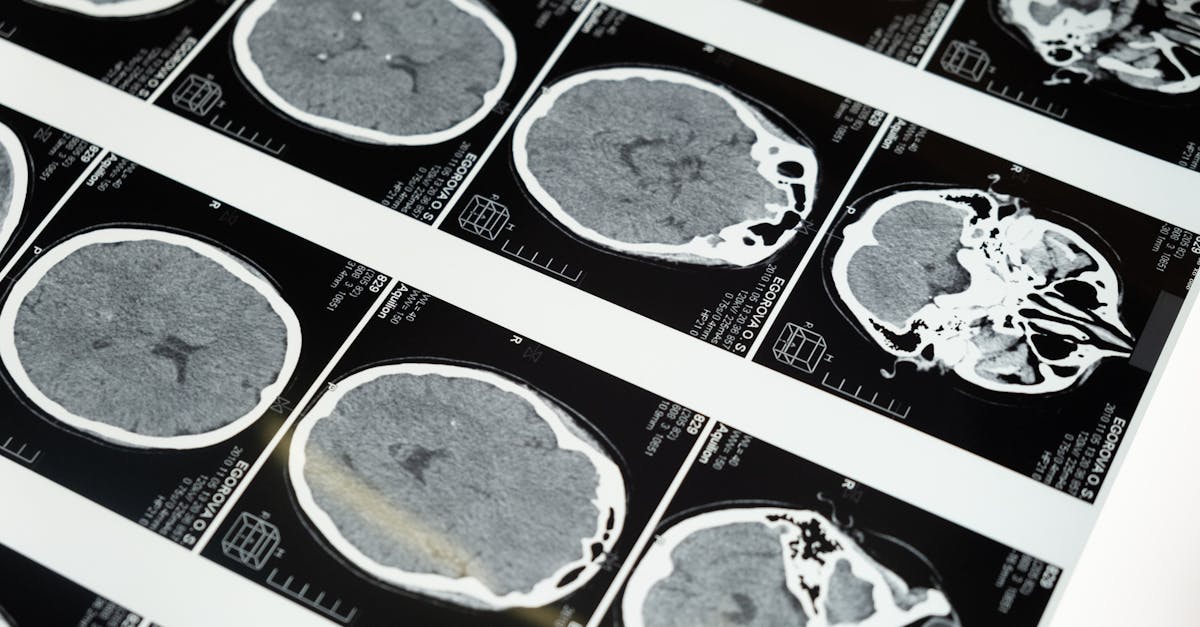
It is also important to note that the interventional radiology is based on multiparametric imaging protocols, which integrate different imaging sequences to provide complementary information. For example, in the context of the treatment of tumor lesions, the combination of the results of a scan at high resolution and magnetic resonance allows more precise determination of tumor volumes before and after intervention.
Following technical progress, the interventional radiology also integrated advanced visualization technologies such as intra-procedure magnetic resonance imaging. This method, although different from conventional approaches, allows dynamic visualization of tissue behavior during the intervention, thus providing an immediate response on the effectiveness of the treatment.
The issues of the interventional radiology are not only limited to techniques and devices but also extend to education and training of practitioners. The integration of these technologies into clinical practice requires constant updating of skills, knowledge of imaging protocols and equipment handling. Thus, the continuing training of radiologists and intervention teams is crucial to guarantee the safety and effectiveness of treatments.
In summary, the interventional radiology is constantly evolving thanks to technological advances, offering less invasive and more precise treatments. Thanks to these innovations, the field of application of this discipline is constantly expanding, meeting the growing needs of modern medicine. It is essential to continue supporting these innovations to improve patient outcomes and expand therapeutic possibilities within medical practice.

Interventional radiology is a specialty that uses medical imaging techniques to guide minimal interventions, allowing various pathologies to be treated in a less invasive manner. The rapid evolution of imaging technologies, the miniaturization of instruments and the improvement of implantable devices have led to significant advances in this area. This article examines advanced techniques in interventional radiology, with emphasis on their impact on clinical practice and patient management.
Advanced visualization techniques
Progress in real-time visualization have transformed interventional radiology. Among recent innovations, FORS (Fluorescence Optical Resonance Scanning) technology, developed by Philips, allows high definition visualization during procedures. This technology combines fluoroscopy with optical techniques to provide real-time images, essential for guiding surgical procedures. Additionally, the use ofsubtraction imaging allows vascular structures to be represented clearly, facilitating angiography and embolization procedures.
Miniaturization of catheterization tools
Miniaturization is a decisive advance in the field of catheterization tools used in interventional radiology. The new ones catheters, thinner and flexible, allow less traumatic insertion for the patient. These modern instruments come with enhanced features, such as built-in sensors to measure pressure or temperature, providing instant feedback on the patient’s condition during procedures.
Developments in implantable devices
Interventional radiology has also benefited from advances in implantable devices such as stents and embolization agents. These devices are designed to effectively treat conditions such as vascular stenoses or arteriovenous malformations. Increasing the biocompatibility and durability of the materials used not only reduces the risk of complications, but also improves long-term patient outcomes. Targeted drug delivery techniques, associated with these devices, are also booming, offering better management of vascular pathologies.
Clinical applications of advanced techniques
The new methods of image guidance have made it possible to broaden the field of application of interventional radiology. Procedures such as biopsy, embolization, drainage of collections and insertion of medical devices are now carried out more efficiently thanks to techniques such asultrasound and the fluoroscopy. These tools enable increased precision while reducing radiation exposure, which is a key issue in protecting patients and medical staff.
Challenges and future prospects
Despite these advances, challenges remain in interventional radiology, particularly in terms of the learning curve of new technologies and patient safety. It is crucial to support the implementation of these innovations through continued training of healthcare professionals and strict safety protocols. The future of interventional radiology seems promising with the emergence of artificial intelligence and image analysis algorithms, which should continue to revolutionize this medical specialty.