Heart failure represents a major challenge in cardiovascular medicine, affecting a significant proportion of the world’s population. Thanks to technological advancements and extensive research, various treatments have emerged to improve the quality of life and sustainability of patients. These treatments include optimization of drug treatment, the use of devices cardiac resynchronization and new pharmacological approaches, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors. Current recommendations emphasize a multidisciplinary approach, integrating education patient and clinical monitoring, in order to optimize the management of this complex pathology.
|
IN BRIEF
|
Heart failure, a chronic disease in constant evolution, requires treatments that adapt to scientific progress and new clinical data. The latest advances in treatments for this pathology focus on new classes of drugs, cardiac resynchronization strategies, as well as an in-depth understanding of the mechanisms of action of treatments. This article highlights recent developments, providing insights into improving clinical outcomes and quality of life for patients.
New drugs and mechanisms of action
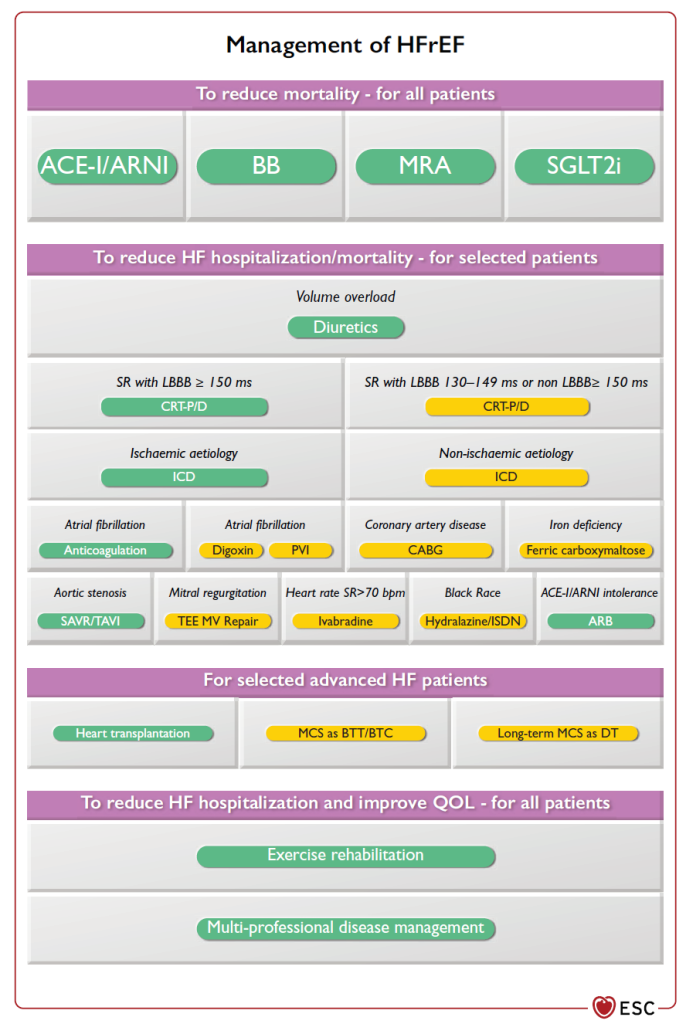
Among recent therapeutic advances, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, such as dapagliflozin, demonstrate significant potential in reducing heart failure symptoms. These drugs work not only by decreasing cardiac volume load, but also by providing metabolic benefits that appear to influence disease progression. Studies have revealed their ability to reduce morbidity and mortality cardiovascular, strengthening their place in the drug treatment of heart failure.
Optimization of drug treatment
Recent recommendations encourage the optimization of drug treatments fundamental, which include diuretics, beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors). Emphasis is placed on the importance of adapting these treatments according to the evolution of the patient’s clinical condition, as well as continuous monitoring of biomarkers. Patient education also takes a central place in the management of heart failure, promoting adherence to treatment and early recognition of signs of decompensation.
Cardiac resynchronization
In cases of advanced heart failure, the cardiac resynchronization through an implantable biventricular pacemaker can provide considerable benefits. This technique helps improve the synchronization of heart contractions, thereby increasing the efficiency of the heart’s pumping. By showing encouraging results, particularly in terms of quality of life and reduction in hospitalizations, this technological approach represents a major advance in the treatment of advanced heart failure.
Heart transplant
For cases of end-stage heart failure, the heart transplant remains the gold standard treatment. The results of this surgical procedure are promising, with long-term survival rates of more than 80% after five years. However, the criteria for selecting donors and recipients continue to evolve, in order to maximize the chances of success and minimize the risks of post-operative complications.
Conclusion on future prospects
Current research aims to explore new molecules and therapeutic combinations, with the aim of expanding the available treatment options. Advances in understanding the mechanisms of action of treatments provide hope for even more targeted and effective therapies. By adopting a multidisciplinary approach that combines medicine, technology and patient education, the future of heart failure treatments looks bright.

Heart failure is a complex pathology requiring a multidimensional therapeutic approach. With recent advances in medical research, new treatments are emerging, improving both the quality of life and the morbidity and mortality patients. This article highlights the main advances in heart failure treatments, including the optimization of drug treatments and new management techniques.
Recent drug treatments
Advances in the field of medicines have led to the development of new therapeutic classes for heart failure. These include sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, such as dapagliflozin, which showed promising results. These medications not only reduce symptoms but also significantly improve patients’ quality of life. Furthermore, angiotensin inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists also continue to play a crucial role in treatment.
Patient education and monitoring
Another major advance lies in the importance given topatient education. The new recommendations emphasize the need for continued education on managing one’s disease. This includes understanding symptoms, the importance of medication compliance, as well as adapting lifestyle to the state of health. At the same time, regular clinical follow-up, with an evaluation of biomarkers, allows treatments to be adjusted according to the progression of the disease.
Cardiac resynchronization technologies
Cardiac resynchronization is another significant advance in the management of heart failure. The use of biventricular pacemakers makes it possible to correct dissociations of cardiac contractions, thus offering patients notable improvements in their cardiac function. This is particularly relevant for patients with advanced heart failure, who see their quality of life improve thanks to this innovative technology.
Heart transplant
For patients with advanced heart failure, heart transplantation remains the standard treatment. Outcomes of surgical procedures have improved significantly over the years, providing patients with increased life expectancy. However, organ availability remains a constraint, prompting consideration of other treatment options more urgently.
Monitoring and integrated management
Finally, the approach multidisciplinary for the monitoring and management of patients with heart failure is also one of the most recent advances. The integration of a team made up of cardiologists, general practitioners, dietitians, nursing staff and health educators makes it possible to offer personalized monitoring adapted to the patient’s needs. This model of care also promotes adherence to treatment and optimization of clinical outcomes.
Recent advances in the treatment ofheart failure represent a significant step towards improving the quality of life of patients. Historically, this condition, which affects millions of people around the world, suffered from a lack of effective therapeutic options. However, recent decades have been marked by the development of new classes of drugs and treatment strategies that have revolutionized the management of this condition.
One of the major areas of innovation is the introduction of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors (SGLT2), of which dapagliflozin has demonstrated promising results. These medications not only relieve symptoms but also play a crucial role in reducing the morbidity and mortality cardiovascular, thus improving the long-term prognosis of patients. This progress demonstrates the importance of clinical research focused on understanding the mechanisms underlying heart failure.
At the same time, therapy by cardiac resynchronization has proven beneficial for patients with advanced forms. The use of dual-cardiac pacemakers has opened an additional avenue of treatment by allowing synchronization of cardiac contractions. This is especially essential for individuals with heart rhythm abnormalities.
In addition, the new recommendations emphasize support holistic, combining patient education, clinical monitoring and biomarkers. These elements are essential to adapt therapies to the specific needs of each patient, thus guaranteeing treatment optimization. With this integrated approach, healthcare professionals can better adapt to the various forms and stages of heart failure.
These advances offer tangible hope to patients and open the way to increasingly personalized and effective therapeutic strategies, making heart failure an increasingly better-controlled disease.