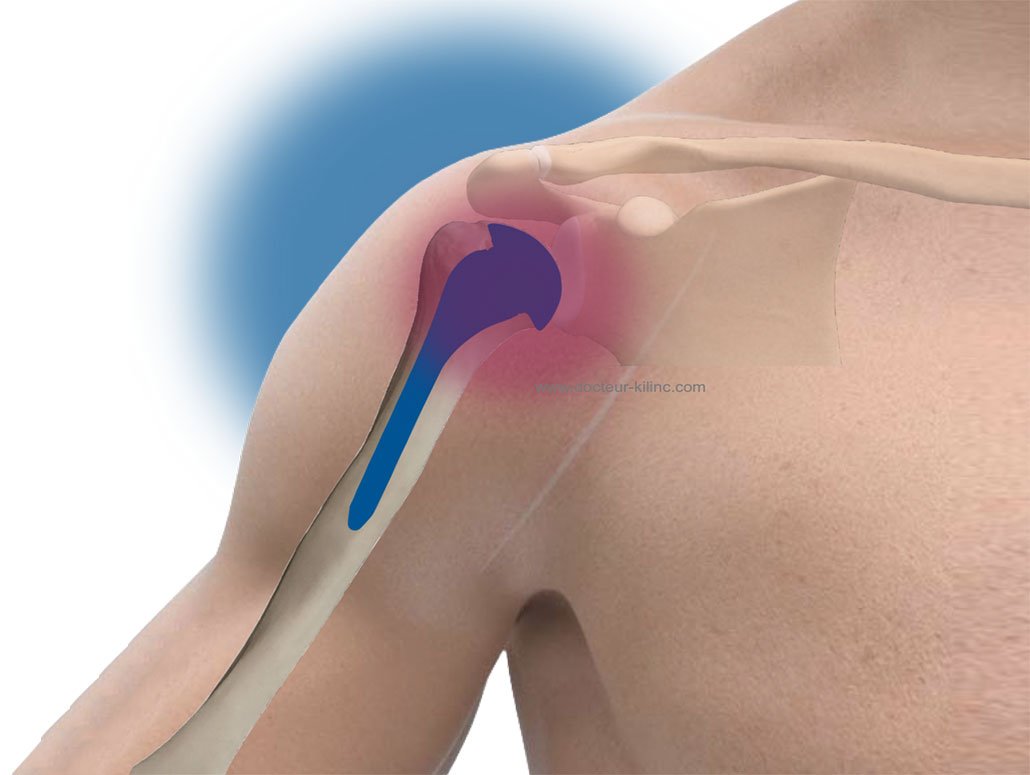
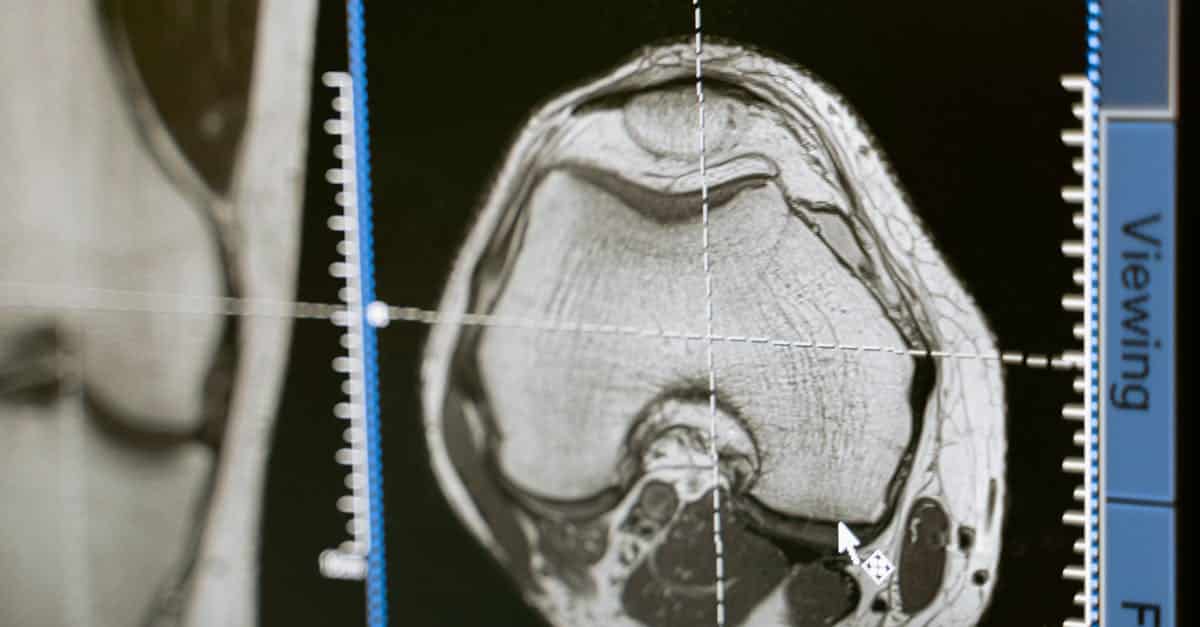
There joint replacement surgery has seen spectacular advances in recent years, significantly transforming the therapeutic pathway for patients suffering from chronic joint pain. Technological innovations, particularly in terms of preoperative planning, made it possible to move from an approach 2D to a method in 3D, offering a more precise vision of patients’ anatomy thanks to tools such as MRI and the scanners. Furthermore, the development of new prosthetics, and the integration of techniques of robotic surgery, contributed to improving the stability of joint reconstructions and reduce postoperative complications, making these procedures safer and more effective. In addition, the indications and results of ankle prostheses and of hip continue to evolve, promising improved quality of life for patients.
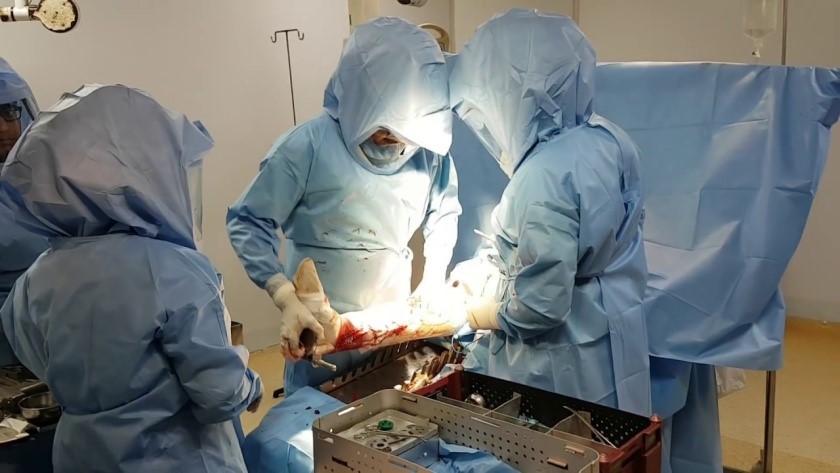
Joint replacement surgery, also known asarthroplasty, has experienced significant advances in recent decades, making it possible to improve the quality of life of patients suffering from chronic pain and functional limitations due to pathologies such asosteoarthritis, THE joint trauma and other degenerative diseases. Thanks to technological progress, innovations in materials and new surgical techniques, this medical specialty has been able to adapt to contemporary health challenges. Improvements in clinical outcomes, prosthesis lifespan and reduction in recovery times are all factors contributing to the growing success of these interventions.
Preoperative planning has been greatly improved, with a move from a traditional 2D approach to 3D planning using scanners and MRI. These advanced technologies allow surgeons to develop precise, personalized models of the joints to be replaced, which optimizes the size, shape and angle of the implants. This three-dimensional planning not only helps improve the precision of interventions, but also reduces intraoperative risks.
THE prosthetics they themselves have undergone remarkable evolution. Materials used for hip, knee, ankle and other joint replacements have been improved, increasing the strength and durability of implants. Titanium and stainless steel are now commonly used, also incorporating components in polyethylene high quality which extends the life of prostheses. Modern implants are designed to better fit the patient’s anatomy, thus promoting more efficient bone integration, often referred to asosseointegration.
Another fundamental aspect of progress in joint replacement surgery is the rise of robotic surgery. Robotics has revolutionized the way surgical procedures are performed. Robotic systems offer a improved control during the operation, reducing the risk of complications and optimizing long-term results. For example, these tools allow surgeons to perform finer movements, minimize tissue damage and make millimeter adjustments during prosthesis implantation. This results in a significant reduction in patient recovery time.
The technique of minimally invasive surgery has also become a standard in the field of joint replacement. Unlike traditional open techniques that involved large incisions, these minimally invasive approaches allow surgical procedures to be performed through smaller incisions. This results in less postoperative pain, a shorter hospitalization and a quicker return to normal activity. Patients thus benefit from a better overall experience linked to the surgical procedure.
Regarding the indications for joint replacement surgery, these have expanded. Prostheses are now recommended not only for elderly patients with advanced osteoarthritis, but also for younger patients suffering from significant functional disability linked to joint damage. Thanks to new surgical techniques and material forbedurations, the longevity of implants is improving, which makes it possible to consider joint replacement for younger populations with active expectations.
A recent study indicates that total hip replacement, for example, has a survival rate >90% after ten years, which underlines the effectiveness of recent innovations. Advances in assessment and management of post-operative complications are also notable. Healthcare professionals use evidence-based practices to minimize the risk of infection, phlebitis or other complications. This helps improve patient satisfaction rates and, therefore, long-term outcomes.
Finally, the development of new replacement prostheses, such as those for the radial head and the distal radioulnar joint, represents a notable advance, allowing more stable and functional reconstructions. Ankle prosthesis, for example, previously suffered from disappointing results, but recent developments have significantly improved functionality and surgical performance. Patients can now look forward to favorable long-term outcomes.
In short, the advances in joint replacement surgery are marked by a multitude of innovations which not only make it possible to meet the growing needs of patients, but also to improve the effectiveness and safety of interventions. The combination of advanced preoperative planning, cutting-edge materials, innovative surgical techniques, and robotics make this specialty a rapidly changing field, offering a promising future for the treatment of joint conditions.

Joint replacement surgery has experienced significant progress thanks to technological innovations and advances in preoperative planning. The evolution of surgical practices now makes it possible to perform less invasive interventions, with improved results, both in terms of functionality and quality of life of patients. This article presents the main advances and recommendations in the field of joint replacement surgery.
Improved preoperative planning techniques
The transition from preoperative planning to 2D to planning in 3D is one of the most notable breakthroughs in surgical procedures. By using MRI images or scanners performed before the operation, surgeons can accurately visualize the patient’s anatomy. This approach makes it possible to optimize the selection of implants and reduce the risk associated with human errors. It also promotes personalization of interventions, guaranteeing a perfect match between the prosthesis and the bone.
Robotic surgery
The advances in robotic surgery represent another major turning point. Robotic systems, like those developed by various industry-leading companies, provide superior control during the operation. This technology makes it possible to achieve unrivaled precision when placing implants, reducing the risk of complications and optimizes the lifetime prostheses. By integrating virtual techniques and real-time training, surgical teams also benefit from a better learning environment, leading to improved surgical performance.
Modern prosthetics and advanced materials
The materials used for prostheses have also evolved, allowing for better bone integration and increased longevity. THE titanium prostheses and innovative composites offer durable solutions adapted to patient needs. Furthermore, the results concerning the ankle prosthesis, once considered unreliable, have improved thanks to recent designs. These new prostheses allow stable reconstructions and functional, bringing a significant improvement in patient mobility.
Post-operative management and rehabilitation
An often overlooked aspect of joint replacement surgery is post-operative management. Protocols of rehabilitation Precise information should be established to optimize recovery and improve functionality. Rehabilitation programs must be personalized according to the type of intervention and the specific needs of the patient in order to promote a rapid return to an active life. In addition, good communication between the patient and the care team is essential to manage expectations and raise awareness about risks and potential benefits.
With the continuous improvement of the techniques and technologies used, joint replacement surgery is constantly evolving. The integration of new practices, such as 3D planning, the use of robots and the optimization of materials, is revolutionizing the field and improving the quality of care. The personalized approach, both before and after the intervention, guarantees a positive impact on patients’ lives, helping them regain mobility and autonomy.