Robotic surgery in oncology is experiencing remarkable advancements, redefining therapeutic approaches for the treatment of cancer. Thanks to technological innovations and the integration of <strongartificial intelligence, this medical discipline offers optimized results in terms of both surgical precision and postoperative recovery for patients. Advanced robotic techniques allow for targeting tumors that are difficult to access while minimizing functional and aesthetic sequelae. Recent research highlights the benefits of robot-assisted surgery, positioning it as a promising solution for the future of oncological treatments.
Robotic surgery in oncology represents a remarkable advancement in the field of cancer treatments. By integrating cutting-edge technologies, it offers more precise and less invasive surgical solutions for various forms of cancer. Recent developments in this sector have improved outcomes for patients, optimized surgical techniques, while reducing complications and recovery times.
One of the major innovations is the use of advanced robotic systems that allow surgeons to perform interventions with increased expertise and precision. For example, robots like da Vinci from Intuitive Surgical have become common tools in cancer treatment, particularly for prostate or gynecological surgeries. These robots facilitate a much clearer three-dimensional vision and manipulation of instruments using finer movements than a human surgeon can generally achieve.
The benefits of robotic surgery for patients are significant. Not only does it reduce surgical stress, but it also minimizes the risk of postoperative complications such as infections, pain, and bleeding. Moreover, the length of hospital stay is often shortened, and the return to daily activities occurs more quickly. These factors contribute to a notable improvement in the quality of life of patients.
The RODEO project, for example, aims to integrate artificial intelligence systems into robotic surgery to transform the traditional surgical approach. This project is accompanied by a collaborative acceleration program that encourages innovation in surgical robotics. Support from the Institut Universitaire de France has also helped lay solid foundations for these high-tech research efforts.
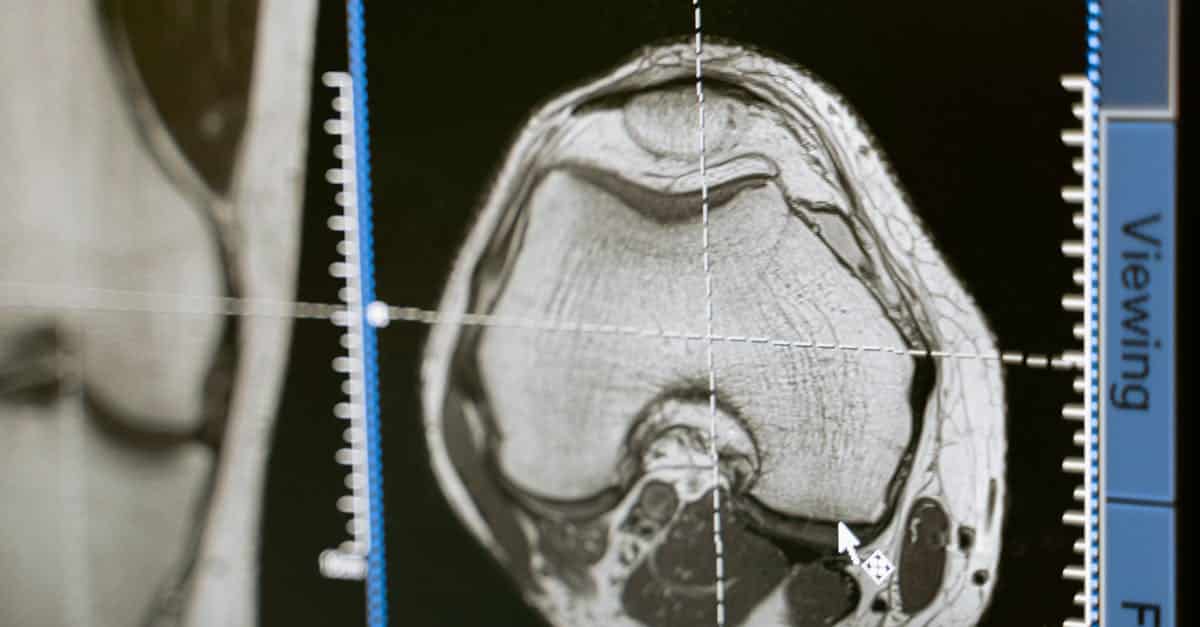
Recent advancements in oncology were revealed at ESMO 2024, showing that even more targeted and personalized treatments are being developed. A striking example is the Epione® solution, which combines advanced robotics with image fusion, allowing clinicians to target difficult-to-reach tumors with incredible precision, particularly in abdominal cancers. This type of innovation highlights the capacity of robotic surgery to overcome challenges that were previously considered insurmountable.
Robot-assisted oncological surgeries have also given rise to a multitude of new surgical techniques. Compared to traditional approaches, robotic surgery offers unmatched precision, essential for complex interventions such as those concerning tumors in sensitive areas. The use of robotic systems allows for more precise movements, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues while ensuring the complete removal of cancerous cells.
A key aspect of advancements in robotic surgery is the evolution of surgical training. With the introduction of robotics into operating rooms, it is crucial that practitioners are trained not only in the use of the tools but also in interpreting the data provided by the accompanying AI. This shift in current training aims to ensure that surgeons are equipped to leverage new technologies that are redefining modern medicine.
It is also important to consider the technological challenges associated with surgical robotics. The need for regular maintenance of robotic systems is crucial to ensure the safety and efficacy of interventions. Equipment may require frequent recalibration, and surgical teams must be trained to address any potential technical issues that may arise during an operation.
Robotics continues to make minimally invasive surgery increasingly accessible, allowing surgeons to tackle complex cases with fewer incisions. The minimally invasive approach not only reduces the risk of complications but also contributes to a faster recovery time for the patient. These technological challenges also stimulate initiatives such as the Grand Challenge “Robotics in Surgery / Enhanced Operating Room”, which is launched to encourage innovation in the field of robotic surgery.
Potential disadvantages associated with robotic surgery procedures, such as the high costs of equipment and limited accessibility, are also elements to be considered. It is essential to weigh these aspects against the potential benefits for patients.
In conclusion, the latest advancements in robotic surgery in oncology herald a new era in cancer treatment. Advanced robots are revolutionizing surgical techniques while making interventions less invasive and more effective. By keeping pace with innovations, maintaining standards of excellence in training, and addressing the challenges related to maintenance and costs, robotic surgery could redefine the landscape of modern medicine and significantly improve outcomes for patients. Ongoing work on robotic innovations and associated techniques will bear fruit in the coming years, further transforming how cancers are approached and treated.

Introduction to Robotic Surgery in Oncology
Robotic surgery represents a major advancement in oncological care, enabling surgeons to perform interventions with unmatched precision. With sophisticated robotic systems, it is now possible to carry out complex procedures while minimizing the risks associated with the operation. This article presents the latest advancements in robotic surgery in the field of oncology, while highlighting the benefits for patients, the challenges to overcome, and future perspectives.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery for Cancer Treatment
Robot-assisted surgery offers several notable advantages for cancer treatment. First, it allows for a minimally invasive approach, thereby reducing postoperative recovery time for patients. This type of intervention is associated with a decrease in postoperative pain, facilitating rapid rehabilitation. Moreover, the increased precision of robotic movements minimizes damage to neighboring tissues, contributing to better oncological outcomes, particularly in terms of survival rates and local-regional control of tumors.
Recent Technological Innovations
The latest advancements in the field of surgical robotics include the integration of artificial intelligence to optimize surgical protocols. Research projects such as the RODEO Project focus on the development of embedded systems that enhance the capabilities of surgical robots. These technologies not only improve preoperative planning but also refine surgical maneuvers in real-time.
Better Training for Surgeons
To fully leverage these new tools, it is essential to train surgeons in robotic techniques. Various training programs are now being implemented to familiarize practitioners with the specifics of robotic surgery. Simulations and hands-on training play a crucial role in mastering these technologies, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of interventions. Collaboration between technical and medical teams also becomes critical for the adequate integration of robots into operating rooms.
The Challenges of Robotics in Oncology
Despite significant advancements, robotic surgery faces several challenges. One of the main obstacles remains the high cost of robotic equipment, which can limit their adoption in certain healthcare facilities. Additionally, the need for specialized technical expertise to operate these systems can create inequalities in access to the best surgical techniques. Long-term studies are also essential to evaluate the overall impact of this technology on clinical outcomes.
Future Perspectives
In the future, robotic surgery in oncology will continue to evolve with the emergence of new technologies. Research on portable robotics systems and devices integrating advanced visualization technologies promises to further transform the surgical landscape. The interconnection between robotic tools and imaging systems via image fusion is another avenue that could allow for more precise targeting of tumors, making interventions even more effective.