The integration of telemedicine in a general medicine practice represents a significant advancement in access to care. For effective implementation, it is necessary to assess the needs of patients and determine the appropriate use cases. In parallel, organizing a secure virtual consultation space will facilitate exchanges between the doctor and their patients, while respecting the care pathway. This approach allows for the treatment of various issues, making medicine more accessible, particularly in areas where access to specialists is limited.
Integration of Telemedicine in a General Medicine Practice
Telemedicine has become an essential component of modern healthcare, particularly in the context of the challenges posed by access to care in certain geographical areas. Integrating telemedicine within a general medicine practice requires a methodical and thoughtful approach. This process involves several key steps ranging from needs assessment to the implementation of appropriate technologies, while also respecting current regulations.
To begin with, it is imperative to determine the objectives of this integration. Physicians must consider the use cases that justify resorting to telemedicine, whether for remote consultations, post-operative follow-ups, or the management of chronic diseases. Identifying these specific needs will optimize the use of digital tools and target patient expectations.
Another important step is to choose the appropriate tools to facilitate the practice of telemedicine. It is recommended to select platforms that offer features such as online appointment scheduling, secure consultation spaces, and protected communication. The data security standards must also be central to this reflection. This includes compliance with GDPR and other regulations regarding the protection of patients’ health information. Platforms like Doctolib or those offered by specialized startups can provide suitable solutions.
Once the tools are selected, it is crucial to train medical and administrative staff in their use. Team members must understand not only how the software works but also the legal and ethical implications associated with telemedicine. Ongoing training and updates in digital skills are undeniably necessary in a constantly evolving field.
Another aspect to explore is the information and education of patients. It is essential to explain the benefits and workings of telemedicine. Information brochures, presentations during regular visits, and online resources can be made available to reassure and encourage patients to adopt these remote consultation methods. Investing in information campaigns can help increase patient participation, particularly for those living in areas with limited access to care.
The booking system must also be adapted to integrate the possibility of phone or video consultations. This involves establishing a clear and smooth appointment scheduling plan. Patients should be able to easily choose between an in-person consultation and a remote consultation according to their convenience and the nature of their health issue.
It is imperative to regularly evaluate the effectiveness and satisfaction of patients regarding telemedicine. This can be done through questionnaires, follow-up interviews, or analyses of service usage data. These feedback experiences are essential to adjust care protocols and improve the quality of services offered remotely. Moreover, physicians must remain attentive to changes in the regulatory framework concerning telemedicine, taking into account the recommendations from public health authorities.
Telemedicine also presents opportunities for interdisciplinarity. Collaborating with other healthcare professionals through tele-expertise or consultation meetings can enrich the care provided to patients. This calls for a multidisciplinary approach that optimizes the management of chronic diseases while enabling knowledge and expertise sharing.
Finally, it is essential to evaluate the impact of telemedicine on the internal functioning of the practice. Establishing processes to ensure continuity of care is necessary, as is establishing protocols for regular follow-ups for patients being monitored remotely. This ensures that consultations do not become isolated but fit into a coordinated care pathway, maintaining constant contact with the treating physician.
All these steps constitute a roadmap to follow for integrating telemedicine in a general medicine practice. This discipline helps improve accessibility to care for many patients, particularly those living in medical deserts, and diversifies care methods while respecting the requirements and standards of quality care.
On the scale of telemedicine, there are different types of services that general practitioners can consider, such as remote monitoring of patients with chronic illnesses. This approach allows for regular and adequate follow-up while reducing the need for frequent patient travel. The use of connected medical devices plays a crucial role in collecting health data remotely, which can then be used by physicians to adjust treatments.
The development of telemedicine must occur within an appropriate framework that includes evaluating funding modalities to ensure economic viability for the practice. Negotiating with health insurance organizations is a crucial step to ensure that remote consultations are recognized and reimbursed. In this regard, it is advisable to study the remuneration models applied by different health systems.
In conclusion, integrating telemedicine into a general medicine practice is a project that requires planning, well-trained human resources, and a robust technological framework. This process is of paramount importance in a context where patient expectations are evolving and access to care is becoming a major concern. Telemedicine, if implemented correctly, can transform medical practice, making care more effective, accessible, and patient-centered.
Telemedicine is establishing itself as an essential tool in the practice of general medicine, facilitating access to care and improving patient management. The integration of this technology into a medical practice requires a methodical approach, respecting the legal and ethical framework while ensuring the quality of care. This article presents practical recommendations for successfully implementing telemedicine in a general medicine practice.
Assessment of Needs and Objectives
Before integrating telemedicine, it is crucial to assess the needs of your patient base and the objectives of your practice. Identify appropriate use cases for teleconsultations, such as monitoring chronic diseases or general medical consultations. Also, consider the specifics of your practice, particularly the demographics of your patients and their comfort level with digital technologies.
Choice of Technology and Tools
For an effective implementation of telemedicine, the choice of tools is essential. Opt for secure platforms that comply with current regulations, ensuring the protection of patients’ personal data. There are different solutions on the market, ranging from video conferencing applications to integrated medical practice management systems. Evaluate the features of each tool to ensure it meets the identified needs.
Staff Training
The integration of telemedicine requires adequate training for medical and administrative staff. Ensure that all team members are familiar with the chosen technological tools and understand the telemedicine protocols. Organize regular training sessions to maintain up-to-date expertise and provide staff with the autonomy necessary to manage remote consultations.
Integration into the Care Pathway
Telemedicine must integrate harmoniously into the coordinated care pathway. It is fundamental to keep the patient’s orientation by the treating physician, ensuring regular follow-up and continuity of care. Plan to work closely with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive monitoring of patients, facilitating the exchange of information via telemedicine.
Communication with Patients
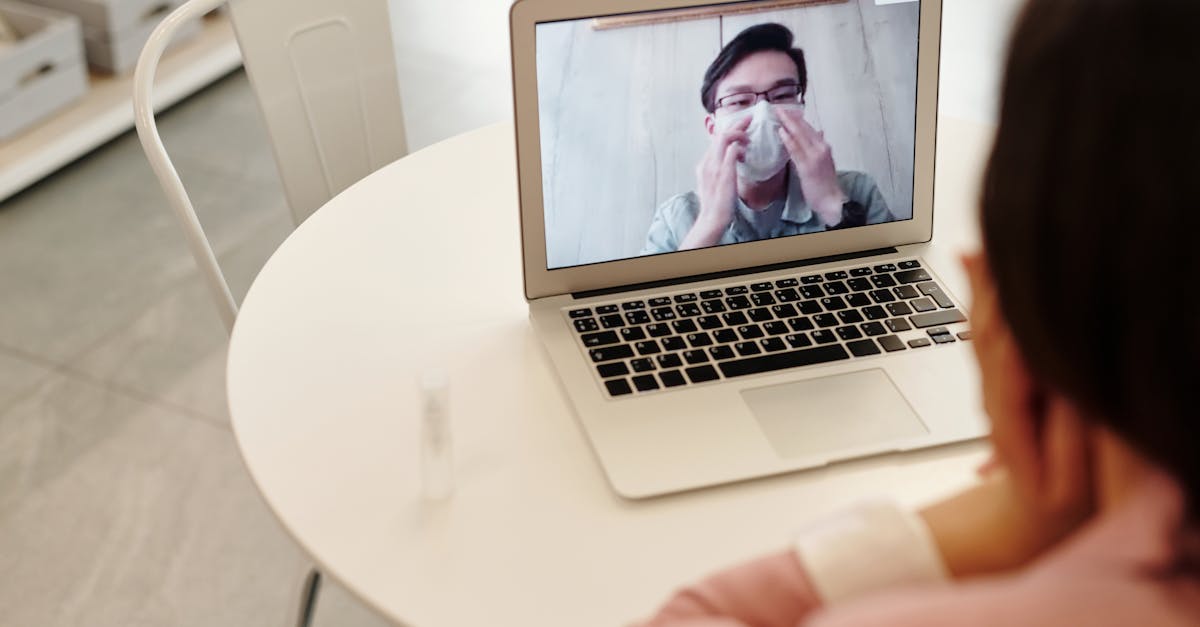
Informing and training patients on the use of telemedicine is crucial to ensure a good experience. Provide clear explanations about how teleconsultations work, as well as the benefits they can bring. Encourage patients to ask questions and express their concerns. You can also create informational materials or video tutorials to help them adapt to this new consultation method.
Evaluation of Results and Adjustments
After the implementation of telemedicine, it is important to conduct a regular evaluation of the results obtained. Gather feedback from both patients and staff members to identify strengths and areas for improvement. Based on the feedback, adjust your practices and the tools used to ensure optimal care quality and adapt the telemedicine offering to the emerging needs of your patients.