Modern surgery has experienced significant advancements with the rise of robotic surgery, offering alternatives to traditional laparoscopy. This technical evolution enables greater precision and better control while reducing complications associated with invasive procedures. In this analysis, we will explore the similarities and differences between these two approaches, highlighting their respective advantages and their impact on patient outcomes.
Surgery is a constantly evolving medical field, and over the past few decades, two major approaches have emerged for performing minimally invasive surgical interventions: robotic surgery and traditional laparoscopy. Each of these techniques has its advantages and disadvantages that deserve analysis in order to better understand their impact on patient outcomes, the duration of interventions, and their recovery.
laparoscopic surgery, known for its minimally invasive nature, was introduced in the 1980s. It relies on the use of small incisions allowing the insertion of a camera and surgical instruments, thus enabling various abdominal procedures. This technique has revolutionized the treatment of many surgical conditions through its numerous benefits, including reduced postoperative pain, rapid discharge from the hospital, and earlier return to normal life.
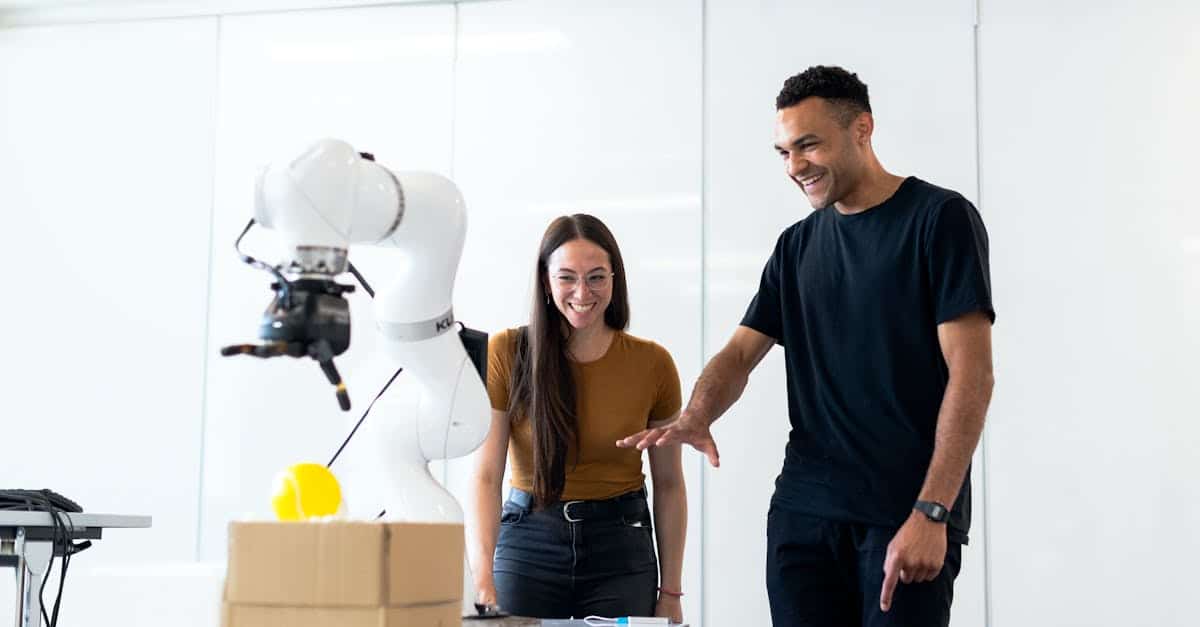
In contrast, robotic surgery, which has gained popularity over the past two decades, uses robotic systems to assist the surgeon during the operation. These systems, such as the renowned Da Vinci Surgical System, provide enhanced control and precision through robotic arms that mimic the movement of human hands. One of the main objectives of robotic surgery is to improve instrument precision and handling, which could reduce complications during and after the procedure.
One of the main advantages of robotic surgery over traditional laparoscopy is the improvement in visualization. With high-definition cameras and optical magnification, surgeons can see anatomical structures with increased clarity, thus facilitating more precise dissection. This visualization capability can also reduce the risk of vascular and nerve injuries, which is particularly crucial in complex procedures related to the prostate or spine.
Furthermore, the maneuverability of surgical tools is another distinctive factor. In traditional laparoscopy, instruments are often limited in terms of movement and angles, which can restrict access to certain anatomical areas. In contrast, robotic surgery allows instruments to perform movements that the human hand cannot, including 360-degree movements. This functionality is particularly beneficial in performing complex procedures, as it allows for finer manipulation.
Despite these advantages, robotic surgery also comes with disadvantages, particularly its cost. The setup of robotic systems and their maintenance can lead to considerable expenses. Additionally, procedures using robots often require extensive training for surgeons, which can pose challenges in terms of accessibility and availability. In contrast, traditional laparoscopy, while lacking the same levels of technology, is generally more widely practiced and accessible in many healthcare facilities.
Another aspect to consider is the intervention time. Studies show that some robotic procedures may take longer than their laparoscopic counterparts. This could be due to the need for surgeons to adapt to the technology and master the use of robotic instruments, which can make robotic surgery less attractive in certain situations where timing is critical.
In terms of postoperative recovery, data is promising for both techniques. Patients who have undergone traditional laparoscopic surgery tend to have shorter hospital stays and faster recovery. However, the results of robotic surgery also show positive outcomes, with often lower levels of postoperative pain and a quicker return to normal daily activities. Studies regularly compare the two methods, and results vary depending on the type of procedure performed.
It is important to note that patient selection plays a crucial role in choosing between these two approaches. Factors such as age, comorbidities, and the location of the pathology must be taken into account to determine the most appropriate surgical method. For instance, in patients with acute conditions or complex medical histories, a traditional approach may be preferred. Conversely, in patients with less complicated conditions, robotic surgery may prove beneficial.
Bariatric surgery is an area where new approaches are observed in the comparison between laparoscopy and robotics. New techniques and complication management are subjects of active research, allowing for continuous evaluation of existing methods.
When addressing areas such as urological surgery, the results show that robotics offers notable advantages, particularly in prostatectomy procedures. The assessment and prospects of robotic surgery in urology are constantly evolving, bringing new perspectives for patients suffering from various urological conditions.
In interventional neurology, the interpretations of results also pose challenges. The use of robotic technologies can significantly influence patient treatment by integrating neuroimaging into complex neurosurgical interventions. This highlights once again the importance of incorporating evidence-based data into the decision-making process regarding the choice between these surgical approaches.
Reconstructive surgery has also benefited from technological advancements. From 3D printing to tissue grafting, innovations remain significant in planning and performing complex interventions. Advances in joint replacement surgery are also notable, with a trend towards less invasive methods that promote improved recovery.
With the rise of artificial intelligence and new technologies, such as 3D printing, surgery is in constant flux. These advances help improve the precision and safety of surgical interventions, both in laparoscopy and robotic surgery.
Ultimately, the choice between robotic surgery and traditional laparoscopy is not an absolute one but depends on several factors, including the patient’s pathology, the type of surgery required, and the available resources. The multiplicity of available techniques pushes healthcare professionals to stay informed about the latest innovations in order to best guide each patient toward the solution most suited to their medical case.
Robotic surgery and traditional laparoscopy represent two major advances in the field of minimally invasive surgery. Although both techniques aim to reduce surgical trauma while improving patient recovery, they differ in their methods, advantages, and disadvantages. This article compares these two approaches, highlights their specificities, and discusses the contexts in which each may be preferable.
Definition of Practices
Robotic surgery uses a robotic system controlled by the surgeon, allowing for increased precision and three-dimensional visualization of anatomical structures. In contrast, traditional laparoscopy, although already less invasive than open surgery, involves the use of manual instruments introduced through small incisions in the abdominal wall, often with two-dimensional vision.
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Among the many advantages of robotic surgery, precision is one of the most notable. Robotic arms can perform finer movements than the human hand, reducing tissue damage and improving outcomes. Additionally, the ergonomics of the command console allow the surgeon to work in a more comfortable position, potentially decreasing fatigue during long operations. The 3D vision and image amplification also provide better depth of field, facilitating delicate interventions, particularly in urology and gynecology.
Benefits of Traditional Laparoscopy
Traditional laparoscopy is often more accessible due to its widespread adoption and the infrastructure already in place in many hospitals. The costs associated with robotic equipment and maintenance can be prohibitive. Additionally, this technique is generally quicker to implement, thereby reducing waiting times for patients. Short-term outcomes in terms of recovery and pain reduction are also comparable to those observed with robotic surgery.
Risks and Limitations
However, each technique carries its own risks and limitations. Robotic surgery may lead to complications related to the equipment, including technical failures that require a quick conversion to an open method. In contrast, traditional laparoscopy, while less complex technologically, sometimes limits dexterity in certain interventions, particularly where narrow access is required.
Clinical Applications and Patient Choice
The choice between these two techniques often depends on the type of intervention, the expertise of the surgical team, and the preferences of the patient. For example, for highly complex procedures such as prostatectomy or interventions on the spine, robotic surgery may offer significant advantages. However, for simpler interventions or when cost is a decisive factor, traditional laparoscopy can be just as effective.
Future of Techniques
The future prospects for robotic surgery appear promising, particularly with the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and augmented reality, which could further improve surgical outcomes. On the other hand, there are ongoing efforts to refine and generalize traditional laparoscopy, optimizing its use in a wide range of procedures.