Palliative care nurses face daily complex challenges related to the management of end-of-life patients. In this context, the use of consolidated dashboards and task automation becomes essential tools to simplify their work. These systems not only allow for the centralization of clinical data but also enable real-time monitoring of patient status, thus reducing the risk of errors and the time spent on administrative procedures. The specific needs of nurses, related to quality of care and human interaction, must be integrated into the development of technological solutions suited to their practice. The integration of these digital tools has therefore become a priority in the evolution of palliative care.
Palliative care nurses clearly express the need for consolidated dashboards integrating various clinical data to better monitor the deterioration of residents. They also emphasize the importance of automation in error-prone areas, such as medication administration and documentation. Despite the challenges related to the use of fragmented technologies and a lack of training, these professionals remain open to the adoption of digital solutions that would facilitate their work and improve the quality of care provided to end-of-life patients.
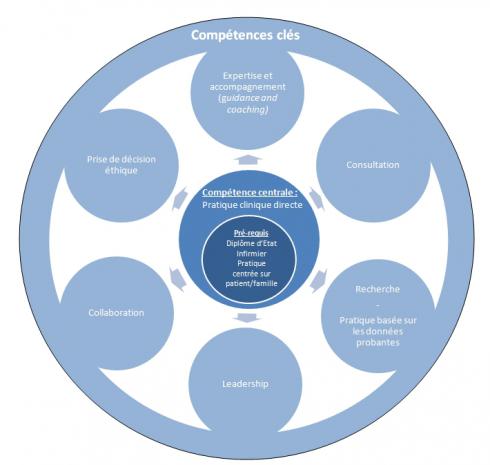
Dashboards: essential tools for palliative care
Dashboards represent an essential aspect of palliative care management. They provide an overview that allows nurses to monitor patient status in real time. By integrating various performance indicators, these tools facilitate informed decision-making, which can have a direct impact on the quality of care provided. Data such as pain levels, hydration, and medication are immediately accessible, helping staff to quickly adjust treatments.
Automation: gaining efficiency
The automation of administrative and documentation tasks is a priority for palliative care nurses. By reducing the time spent on repetitive tasks, they can focus more on assisting patients and supporting their families. This also improves the accuracy of the data collected, thereby limiting human errors. Thus, various automated tools allow for updates to medical information or managing appointments while ensuring optimal continuity of care.
Challenges and future perspectives
With the spread of digital technologies, nurses encounter challenges in integrating these tools into their daily routine. It is essential to take into account the needs and expectations of healthcare professionals to develop suitable solutions. Specific training on the use of dashboards and automated systems should be implemented to overcome these obstacles. This would ensure successful adoption and better adherence to end-of-life care standards.
In the field of palliative care, nurses play a vital role, and dashboards as well as automation have become key tools for optimizing their work. The challenges they face include managing patient information at the end of life and the necessity of smooth communication among the various health stakeholders. By integrating consolidated dashboards that group essential clinical data, nurses can more easily monitor the health status of residents, thus facilitating their decision-making.
Moreover, the automation of repetitive tasks helps reduce the administrative burden on caregivers. For instance, processes such as medication management and clinical documentation can be automated, freeing up time to focus on human intervention and patient-centered care. This approach also provides a solution to human error, promoting better safety in care.
Furthermore, it is imperative that nurses receive adequate training on these digital tools. Continuous technical and educational support is crucial to ensure that these solutions are truly integrated into their daily practice. Implementing targeted training programs on the use of dashboards and automation technologies could greatly enhance the efficiency of care while strengthening caregivers’ confidence in their use.
In summary, the future of palliative care lies in harmonizing automation and dashboards, enabling nurses to deliver quality care while respecting patient dignity. The challenge is to develop tools that are accessible and intuitive, so that nurses can focus on their primary mission: providing empathetic and individualized care.