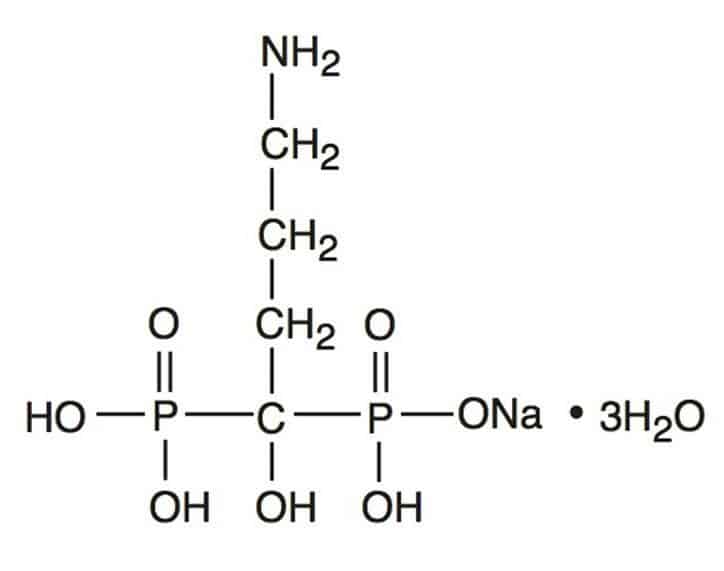
Alendronate is an essential medication in the management of osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women. Indeed, its ability to strengthen bone mass by inhibiting bone resorption makes it a valuable ally in preventing fractures. However, like any medication, it has aspects that require particular attention. The prescription of alendronate requires a thorough evaluation of benefits versus associated risks.
Side effects may vary from one patient to another, with symptoms such as bone pain, vision disorders, or dizziness. Additionally, certain contraindications must be respected, especially in patients with severe renal insufficiency or a history of osteonecrosis. Understanding these aspects is crucial not only to ensure the effectiveness of treatment but also to minimize risks. Addressing these issues is about providing better care to patients and contributing to their well-being. In this context, it is important to explore in depth the medical prescription, associated side effects, and contraindications of alendronate.

Alendronate is a medication belonging to the class of bisphosphonates, widely used for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and at-risk men. Its purpose is to reduce the risk of bone fractures by inhibiting bone resorption, a process that, when unbalanced, can lead to brittle bones. However, like any medication, alendronate requires a medical prescription and is associated with potential side effects as well as contraindications that must be considered by healthcare professionals and patients.
Medical Prescription of Alendronate
The prescription of alendronate is generally reserved for patients presenting risk factors for osteoporosis. This includes older women, especially those who have already reached menopause, as well as individuals with a family history of osteoporosis or other metabolic bone disorders. Before prescribing this medication, a physician must evaluate the bones mineral density of the patient, usually measured by a bone densitometry.
Common dosing recommendations include taking one 10 mg alendronate tablet once a day or one 70 mg tablet once a week. The form and frequency of administration may vary according to the individual’s characteristics and the physician’s recommendations. It is vital that the patient strictly follows the prescription instructions to maximize the medication’s effectiveness.
When prescribing alendronate, the physician must also discuss the administration methods. Alendronate should be taken in the morning on an empty stomach with a large glass of water to ensure optimal absorption. Patients should avoid lying down or eating for at least 30 minutes after taking it to prevent gastrointestinal problems, which are among the most common side effects associated with this medication.
Side Effects of Alendronate
The use of alendronate may lead to various side effects, some of which can be more serious than others. Among the most frequently reported side effects are bone pain, joint pain, and muscle pain. These symptoms are observed in a significant proportion of patients, sometimes more than 10% of them. Bone pain can be intense, forcing some patients to adjust their treatment or seek alternatives.
In addition to musculoskeletal pain, other side effects such as dizziness and blurred vision have also been reported. These effects can impair the quality of life of patients, and it is essential that they inform their physician. Regular monitoring is also recommended to detect potentially severe side effects, such as signs of jaw osteonecrosis, which, although rare, constitute a serious complication of bisphosphonate treatment.
Gastrointestinal side effects may also occur, including abdominal pain, heartburn, esophagitis, and other digestive disorders. These symptoms can worsen if the rules for administering the medication are not followed. In this context, patients should be educated about the importance of adhering to the recommendations to minimize these risks.
Contraindications of Alendronate
Alendronate has several contraindications that must be strictly observed to avoid serious complications. For example, this medication is strictly contraindicated in patients with severe renal insufficiency, particularly those with creatinine clearance below 35 mL/min. In these cases, the safety of the medication’s use cannot be guaranteed.
Furthermore, existing hypocalcemia must be corrected before starting alendronate treatment, as insufficient blood calcium levels can lead to complications. Patients with a history of esophagitis or other esophageal disorders may also be at risk, and their treatment should be carefully reviewed.
Concerning rare but serious side effects, practitioners should be particularly vigilant for signs of jaw osteonecrosis or atypical femur fractures, which may occur in some patients undergoing prolonged treatment with bisphosphonates, including alendronate. Regular dental health evaluations are also recommended for patients during their treatment.
Finally, it is important to consider the patient’s complete medical history before prescribing alendronate. Interaction with other medications as well as any potential allergies should be discussed. In summary, the physician must assess the benefits and potential risks of alendronate while considering each patient’s medical specifics.
FAQ about Alendronate: Prescription, Side Effects, and Contraindications
What are the main side effects of alendronate? Patients may experience side effects such as blurred vision, dizziness, and intense bone pain, muscle, or joint pain.
Who should not take alendronate? This medication is contraindicated in individuals with frequent joint swelling, and in rarer cases, it can lead to jaw osteonecrosis or subtrochanteric femur fractures.
How should alendronate be taken to be effective? It is essential to follow the recommendations to ensure adequate absorption. Alendronate should be taken at least 30 minutes before any food or drink.
What patients should be cautious when taking alendronate? Patients suffering from severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 0.58 mL/s) should not use this medication.
What is the main problem faced by patients on alendronate treatment? Patients treated with alendronate often suffer from bone pain, joint, and/or muscle pain, which can be very frequent, exceeding 10% of cases.
How long does treatment with alendronate need to last? It is important that patients take alendronate for as long as their physician prescribes it, considering the risks and benefits of the treatment.