Robotic surgery is emerging as a transformative force in the medical sector, redefining operative practices within healthcare institutions. With technological advancements, robotic systems, such as the da Vinci and other innovative platforms, are proving capable of offering increased precision and improved outcomes for patients. As these technologies become mainstream, the question arises about their standardization in future hospitals. This evolution could ensure a uniform quality of care and an optimization of surgical protocols across various medical specialties, while presenting training and integration demands for medical teams.

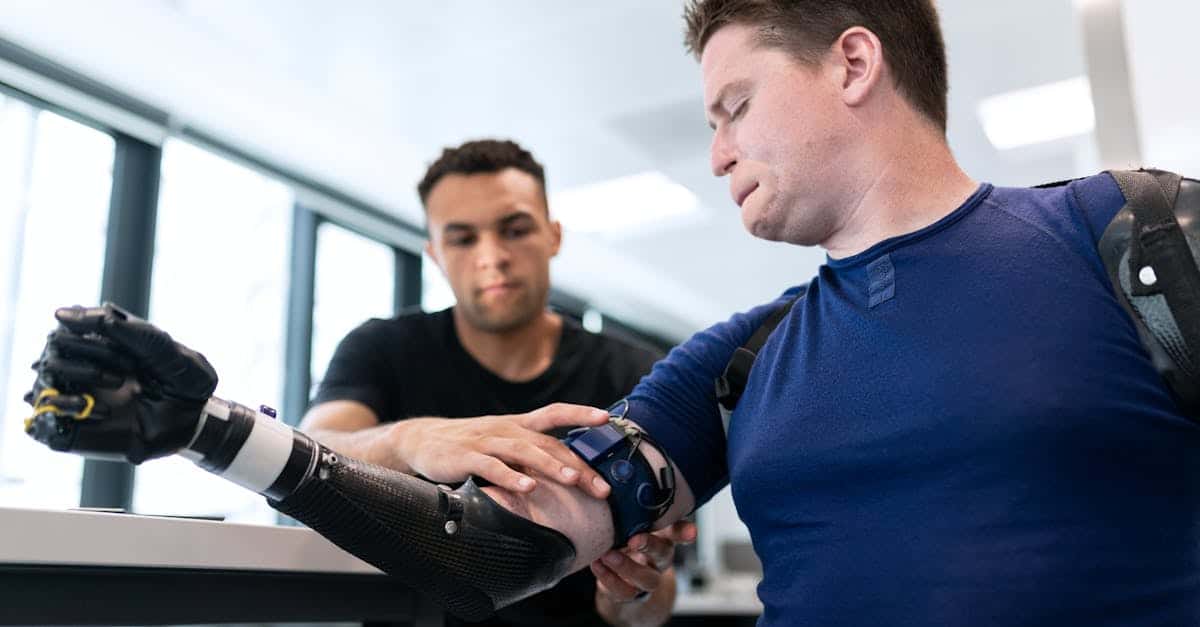
Robotic surgery represents a significant turning point in the medical field, offering possibilities that were previously only imaginable. Currently, robotic systems such as the da Vinci® are at the forefront of technological innovations in hospitals. These tools enable surgeons to perform operations with unparalleled precision, thus opening new perspectives for both reconstructive medicine and more complex interventions, such as oncology. In this dynamic, a crucial question arises: are we moving towards a standardization of robotic-assisted surgical practices in healthcare institutions?
To understand the implications of this standardization, it is fundamental to first examine the technological advancements that have allowed the emergence of robotic surgery. Indeed, progress in imaging, sensors, and artificial intelligence has been decisive in the development of these systems. With robots capable of working in minimally invasive ways, operational risks are significantly reduced, which represents a valuable advantage for both patients and practitioners. For example, the latest generation robots, such as the da Vinci Xi®, allow for complex interventions, thereby reducing recovery times and improving clinical outcomes.
The benefits of robotic surgery are not limited to surgical performance alone. They also have a significant economic impact on the healthcare system. Indeed, while requiring high initial investments for the acquisition and maintenance of robots, these systems significantly enhance the efficiency of procedures; consequently, they can reduce overall costs by decreasing hospitalization durations and postoperative complications. Healthcare institutions are gradually adopting these technologies with the hope that this will lead to long-term savings.
However, this widespread adoption of robotic surgery is not without challenges. If we wish to see these innovations standardized across different hospitals, it will be necessary to establish a clear and effective regulatory framework. The training of medical teams is a key issue, as healthcare professionals must not only master the use of robots but also know how to make the best use of them. Indeed, the implementation of robotic systems requires a cultural and operational shift within hospitals. This transition necessitates training programs and case studies analyzing situations of success and failure in robotic surgery.
In this regard, the analysis of robotic surgery systems highlights situations where effective standardization could benefit both patients and practitioners. For example, surgical protocols could be harmonized to include standardized safety procedures, diversified according to specialties. In this light, a case study on successful interventions and failures in robotic surgery could be undertaken to draw lessons from past experiences and define best practices to adopt.
The challenges related to acquisition and maintenance costs of robotic surgery systems also constitute a crucial point. The overall investment amount for the acquisition and training of medical teams, as recently noted by the AP-HP with its commitment to nine new state-of-the-art da Vinci robots, raises questions about the fair allocation of resources. Indeed, it is clear that not all institutions will be able to equip themselves in the same way, which could contribute to inequalities in access to care.
A significant issue related to standardization is the development of intervention standards. If we want robotic surgery to harmonize on a global scale, then it is crucial to define these standards. These should include both the surgical operative process itself and the associated safety criteria. The diversity of surgical robots on the market makes this task challenging, but essential for informed decision-making by medical teams.
Beyond the technical aspects, one cannot overlook the human dimension in the standardization process. Resistance to change from healthcare professionals can hinder the adoption initiatives of robot-assisted surgery. The implementation of continuous training and motivation programs can therefore facilitate the integration of these innovative technologies. Establishing a climate of trust and acceptance around these systems adorned with advantages could help reduce anxiety and reluctance, thereby facilitating the standardization of practices.
Another point to consider is the impact of robotics on postoperative recovery. Indeed, several studies corroborate that patients who have undergone minimally invasive operations report less pain and smaller scars. These reasons encourage hospitals to adopt these robotic techniques as they can significantly enhance patient satisfaction. A feedback based on analyses of case studies could also demonstrate the successes and failures of these technologies in healthcare.
Finally, the financing of surgical robots and the development of health policies adapted to facilitate their adoption are elements to be incorporated into the overall reflection on robotic surgery. Health investments should not only focus on technology but also on the quality of training and the long-term impacts on patient health. A good long-term strategic plan will involve the allocation of budgets for research, surgeon training, and the development of protocols adapted to the evolution of technologies and patient needs.
Looking ahead, the future development of robotic surgery will undoubtedly lean towards greater automation of tasks. Progress that we must consider through a collaborative approach, bringing together surgeons, engineers, and public health officials to manage the growing challenges posed by the integration of these complex technologies.
The coming years will be decisive for the future of robotic surgery in the hospitals of tomorrow. The potential of this technology is undeniable, but to truly benefit from it, guidelines and policies must promote thoughtful and harmonized integration. In this sense, moving towards a standardization of practices could not only benefit healthcare professionals but especially the patients who expect increasingly tailored and effective care.
Through continuous innovations and the engagement of all stakeholders, the eventual standardization of robotic surgery promises a future where care will be optimized for the well-being of patients. However, this will require constructive exchanges, research, and a commitment to overcoming the technical, logistical, and human obstacles that this transition may generate.
Finally, as robotics continues to advance and evolve, healthcare institutions must remain connected to technological advancements to ensure that a standard of superior quality care is established. The road to effective standardization of robotic surgery may be complex, but it is essential for enriching the therapeutic experience of patients and improving overall health outcomes.

Robotic surgery establishes itself as a major advance in the medical field, transforming traditional operative practices. In this article, we will examine how the standardization of robotic surgery techniques in tomorrow’s hospitals could improve clinical outcomes, optimize processes, and enhance patient safety. Recommendations will be proposed to facilitate this transition and ensure effective adoption of these technologies in the hospital environment.
The Benefits of Standardization
The standardization of robotic surgery techniques could yield several benefits, both for surgeons and patients. First, it would promote better training for medical teams by allowing each surgeon to acquire a uniform mastery of robotic systems. This would also increase patient confidence, who would be reassured by the expertise of a team that has followed a standardized protocol.
Moreover, standardization would help reduce medical errors, as each intervention would be performed according to precise guidelines, thus minimizing the risks of unexpected variations in operative techniques. This would be particularly beneficial in complex specialties such as oncological surgery or bariatric surgery, where mastery of the tools is essential to ensure patient safety and the success of the procedure.
Development of Training Protocols
To implement effective standardization, hospitals must invest in the development of robust training protocols for surgeons. These protocols should include theoretical courses, practical training on simulators, and sessions for learning about the specific robotic systems used in the institution. It is crucial to establish continuing education programs to ensure that surgeons remain informed about the latest innovations and techniques.
By integrating training modules on the theoretical and practical aspects of robot-assisted surgery, hospitals can ensure that all practitioners possess the necessary skills to use these technologies effectively and safely.
Performance Evaluation and Feedback
An essential aspect of standardization is the ongoing evaluation of surgical performance. Medical institutions must establish monitoring and evaluation systems that collect data on the outcomes of interventions performed by robotics. This data should include success indicators, such as complication rates, lengths of hospital stay, and patient satisfaction levels.
Feedback from surgeons about their interventions also allows for the assessment of the effectiveness of standardized protocols. By organizing regular meetings to discuss cases and outcomes, teams can identify areas needing improvement and adjust practices accordingly.
Integration of Technology and Interdisciplinary Collaboration
The hospitals of tomorrow must foster a culture of technological integration and interdisciplinary collaboration. This involves bringing together teams composed of surgeons, nurses, biomedical engineers, and computer specialists to design customized protocols tailored to the needs of the institution. Exchanges and cooperation between different specialties will optimize the use of robotic systems while considering the specifics of each discipline.
The establishment of committees or working groups dedicated to surgical robotics in hospitals can facilitate this collaboration and ensure that standardization is adopted uniformly and effectively across all fronts.