The medical prescription of aripiprazole requires special attention due to its potential side effects and contraindications. Used to treat disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, this medication works by altering the chemical mechanisms in the brain. Although it may offer benefits in managing symptoms, it is essential to be aware of adverse reactions that may occur in some patients. Each prescription must be carefully evaluated, taking into account the associated risks and the overall health of the patient.
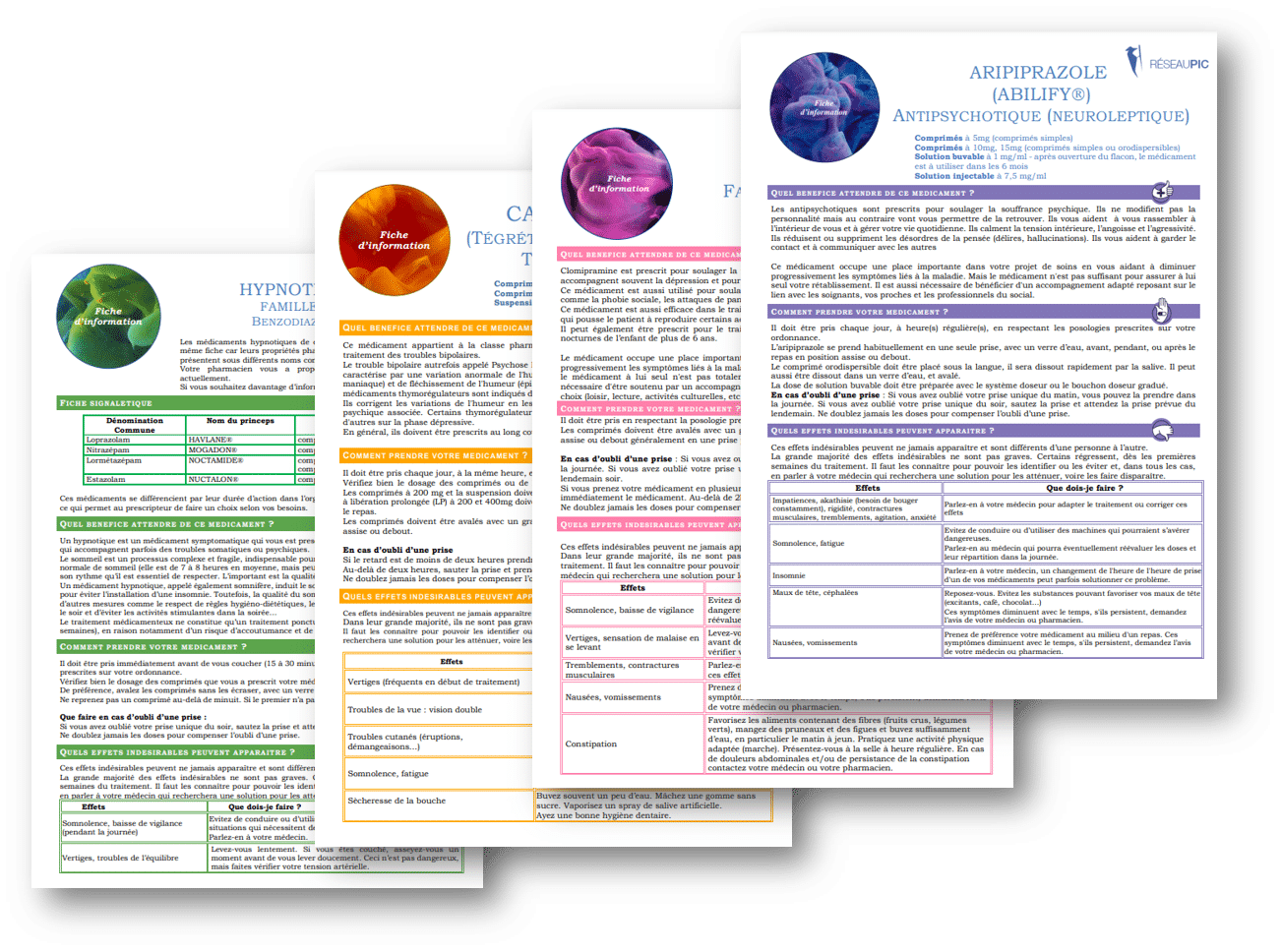
Aripiprazole is a medication that belongs to the class of antipsychotics. Its primary use concerns the management of mental disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. However, this medication may also be prescribed as an adjunct to other treatments for patients suffering from major depressive disorder who show an insufficient response to previous treatments. A good understanding of the prescription, potential side effects, and contraindications of aripiprazole is essential for safe and effective use.
Indications and Medical Prescription
When a doctor considers prescribing aripiprazole, they must assess the overall mental health of the patient as well as their medical history. The standard initial dosage for an adult with schizophrenia is often set between 10 mg and 15 mg per day, which can be adjusted according to individual needs. To meet the needs of adolescents, the starting dose may begin at 2 mg, and then adjust the dose in the following weeks as needed based on the response to treatment.
For bipolar disorder, the recommended initial dose for adults is typically 15 mg per day, with possible adjustments up to a maximum of 30 mg per day. Adolescents, on the other hand, should start with lower doses to avoid any potential risk of significant adverse effects.
Side Effects and Medical Monitoring
Like many medications, aripiprazole can cause side effects. Some effects may be mild while others may require immediate medical attention. Studies show that at least 1% of patients taking this treatment report side effects such as agitation, anxiety, difficulty sleeping, headaches, or gastrointestinal disorders, including nausea or vomiting.
In the long term, more serious side effects may occur, raising concerns for the patient. Symptoms such as abnormal movements or muscle contractions (often referred to as extrapyramidal symptoms) may manifest. Additionally, it is possible to observe significant changes in the patient’s weight, leading to health issues associated with obesity.
Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is therefore essential. Doctors must regularly assess the impact of aripiprazole on the patient by monitoring the onset of side effects and the effectiveness of treatment. If concerning symptoms arise, such as suicidal thoughts, increased agitation, or behavioral changes, it is crucial to inform a doctor immediately.
Contraindications and Precautions for Use
There are clear contraindications for the use of aripiprazole. Anyone with a known hypersensitivity to aripiprazole or any of its components should not use it. Other medical conditions may also make the use of this medication problematic. These include a history of strokes, cardiological disorders, or episodes of coagulation disorders. Additionally, caution should be exercised for those with a history of epilepsy or seizures.
Patients with metabolic disorders such as diabetes should be cautious since aripiprazole can cause increases in blood sugar levels. It is therefore recommended to regularly monitor the blood sugar of patients during treatment. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also discuss the potential risks associated with this medication with their doctor, especially if pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Finally, it is vital to inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter medications, as certain interactions may alter the effectiveness of aripiprazole or increase the risk of side effects. In summary, medical follow-up and open communication are essential to ensure the success of treatment with aripiprazole and minimize risks.
FAQ about Aripiprazole
Q : What is aripiprazole?
A : Aripiprazole is an antipsychotic medication used to treat disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It may also be used as an adjunct in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
Q : How does aripiprazole work?
A : This medication helps manage symptoms by modifying the actions of certain chemical messengers in the brain but does not constitute a curative treatment for medical disorders.
Q : What are the possible side effects of aripiprazole?
A : Side effects may include: agitation, anxiety, drowsiness, constipation, dizziness, skin rashes, among others. Some effects may require medical consultation.
Q : Who should not take aripiprazole?
A : Aripiprazole is not recommended for individuals with a allergy to this medication or any of its ingredients. Other health conditions should also be considered before prescribing.
Q : What is the recommended dosage for aripiprazole?
A : For adults with schizophrenia, the recommended dose is generally between 10 mg and 15 mg per day, with a maximum of 30 mg. Adolescents may start with 2 mg per day with possible increases.
Q : What warnings should be considered when using aripiprazole?
A : It is essential to inform the doctor of any medical condition or allergy, especially in case of a history of heart disease, diabetes, or swallowing problems. Strict monitoring may be required for these conditions.