Prescribing medications is a delicate act that requires a thorough understanding of the medications in question. Among these, the furosemide, A diuretic widely used, deserves special attention due to its potential effects on patient health. This medication is commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as edema linked to heart disease andhigh blood pressure. However, its use is not without risks. Adverse effects, includinghypokalemia—a decrease in the level of potassium in the blood—, as well as other complications such ashypotension and thehyperuricemia, may occur. In addition, some contraindications absolute, such asanuria, there tear or severe liver disorders, require particular vigilance when prescribing. To ensure optimal use of furosemide, it is crucial to know these parameters and carefully assess the benefit-risk ratio before treatment. Understanding the indications, side effects and contraindications is therefore essential to guarantee the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
Medical prescription of furosemide and its implications
Furosemide, marketed under several names including FUROSEMIDE BIOGARAN, is a diuretic medication widely prescribed to treat a variety of conditions. Its medical prescription revolves around its main use for the control of edema, which can result from heart, kidney or liver diseases, as well as for the management ofhigh blood pressure. This medication works by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and water in the kidney tubules, thereby increasing the volume of urine and making it easier to remove excess fluid from the body.
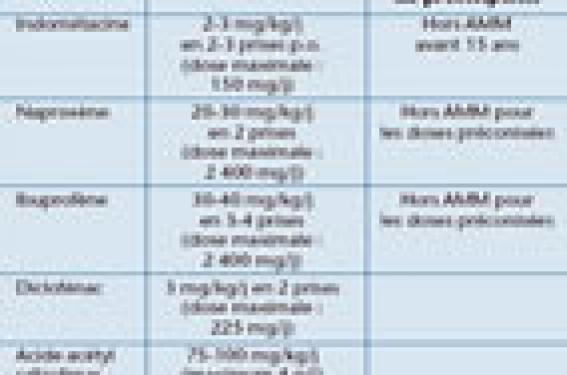
The dosage of furosemide should be adjusted for each patient, based on careful assessment of their overall health, renal function and test results. Physicians should be careful when initiating treatment, considering the patient’s weight and the degree of the condition being treated. Regular monitoring is essential for possible oscillations in electrolyte balance and blood pressure.
Side effects of furosemide
Despite its considerable beneficial effects, furosemide is not free of adverse effects. THE side effects the most common includehypokalemia, or a decrease in the level of potassium in the blood, which can have serious consequences for heart health. Patients should have their potassium levels monitored regularly, especially during prolonged administration or at high doses.
Besides hypokalemia, other complications such ashyponatremia, a reduction in sodium in the blood, and thehyperuricemia, increased uric acid levels, may manifest. Symptoms of electrolyte imbalances may include muscle cramps, excessive fatigue, and trouble concentrating. Some patients may also experience dizziness or hypotension as a result of excessive dehydration due to increased diuresis.
Allergic reactions may also occur, particularly in individuals with a history ofhypersensitivity to one of the active substances of the medicine. In extreme cases, these reactions can manifest as severe skin rashes and breathing problems. Healthcare professionals must be vigilant in the face of these clinical manifestations. Discontinuation of the drug should be considered if such effects occur.
Contraindications and precautions for use
Furosemide has a number of contraindications absolute. It should not be administered to patients withanuria, where the kidneys no longer produce urine, nor to those with dehydration or a hepatic encephalopathy, a neurological condition associated with severe liver disease. Careful medical history screening is crucial before prescribing this medication.
Additionally, furosemide should be avoided in individuals who have developed galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or certain hereditary diseases that prevent the absorption of sugars. Diabetic patients should also be monitored closely, as furosemide may interfere with blood sugar control.
There medical supervision is essential for all patients undergoing treatment with furosemide, particularly those with renal or hepatic insufficiency. Regular blood tests help monitor electrolyte balance and kidney function. Particular care should be taken when using other drugs that may interact with furosemide, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or certain antibiotics.
Ultimately, prescribing furosemide must be accompanied by a careful assessment of all potential risks. The healthcare professional must be able to clearly inform the patient of the need for close monitoring and of the signs to watch for during treatment. This vigilance ensures safe and effective management of the conditions for which this diuretic is prescribed.

FAQ on Medical Prescription, Side Effects and Contraindications of Furosemide
What is the main indication for furosemide? This medicine is mainly prescribed to treat edema associated with conditions such as heart failure and to managehigh blood pressure.
What are the potential side effects of furosemide? Side effects may include hypokalemia (decrease in potassium in the blood), dehydration, hypotension, as well as electrolyte disorders such as hyponatremia And hyperuricemia.
What are the contraindications to furosemide? This medication is strictly contraindicated in cases ofanuria, of dehydation, ofhepatic encephalopathy and in people with hypersensitivity known to the active substance.
Can furosemide be used during pregnancy? Its use should be avoided because it may be linked to risks for the fetus, which can lead to fetoplacental ischemia and a risk offetal hypotrophy.
Are there any interactions with other medications? Yes, furosemide can interact with many other medications. It is important to inform the doctor of all current treatments to avoid serious side effects.
How should the dosage of furosemide be adjusted? The dosage should be adjusted according to the clinical reaction patient, laboratory test results and underlying health conditions. Regular monitoring is recommended.
What are the symptoms of a furosemide overdose? Symptoms may include disorientation, symptoms of hypokalemia such as muscle weakness, cramps, and heart problems. If in doubt, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional immediately.