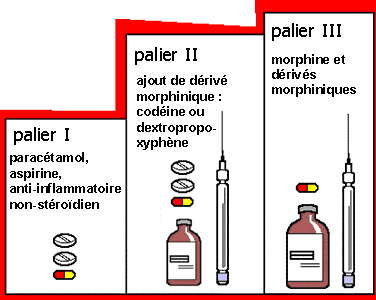
The use of codeine as an analgesic and antitussive is governed by a strict medical prescription due to potential side effects and associated contraindications related to this substance. Although codeine provides relief from pain and cough symptoms, it can also lead to undesirable effects such as drowsiness, constipation, and more severe risks in cases of overdose. Some patients, particularly those suffering from respiratory issues or dependencies, must exercise particular caution regarding its use.
Codeine is a pain reliever and antitussive of natural origin, primarily prescribed to relieve pain and treat dry coughs. Although it offers beneficial effects within the framework of appropriate medical treatment, its consumption must be closely monitored given the associated risks of its use. This article aims to provide an overview of the prescription of codeine, its side effects as well as its contraindications.
Side effects of codeine
Like any medication, codeine has side effects that deserve particular attention. The most common undesirable effects are as follows:
1. Constipation: Codeine can slow down intestinal transit, leading to constipation problems. This phenomenon is particularly frequent in patients who use codeine for long periods.
2. Drowsiness: This medication can induce feelings of fatigue and drowsiness, thereby affecting alertness and the ability to perform tasks requiring a good level of concentration, such as driving or operating machinery.
3. Nausea and vomiting: The use of codeine can cause nausea and vomiting, especially when initiating treatment or in cases of overdose. It is essential to inform the doctor if these symptoms become problematic.
4. Respiratory issues: In case of overdose, codeine can lead to respiratory issues. This may present as slowed breathing, and even respiratory arrest in the most severe cases. Therefore, it is crucial to adhere to the prescribed doses.
5. Allergies: Although rare, allergic reactions may occur. These reactions can range from mild rashes to more severe reactions, such as angioedema. In case of signs of allergy, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional immediately.
6. Dependence: Prolonged use of codeine over a long period can lead to physical or psychological dependence. This becomes a notable concern in patients with a history of dependency or psychiatric disorders.
The importance of medical supervision is therefore paramount, especially in individuals with particular susceptibilities or using other medications that may interact with codeine.
Contraindications of codeine
Before prescribing codeine, it is essential to consider certain contraindications to ensure patient safety:
1. Hypersensitivity: Codeine is contraindicated in cases of known hypersensitivity to the molecule or to any of the excipients in the medication. An allergic reaction may occur, rendering the use of this treatment inappropriate.
2. Asthma: Asthmatic patients or those at risk of bronchospasm should not use codeine, as it can cause respiratory issues. The depressant effects on breathing can worsen the condition of a patient suffering from a respiratory disease.
3. Severe hepatic or renal insufficiency: Individuals with impaired liver or kidney function should avoid codeine. The degradation and elimination of the medication may be compromised, leading to an increased risk of toxicity and undesirable effects.
4. Respiratory and convulsive disorders: Patients with a history of respiratory problems or convulsions should be excluded from codeine prescriptions. These disorders may be exacerbated by the effects of codeine.
5. Prior medical consultation: Before initiating treatment with codeine, patients are advised to discuss their overall health status, all medications being taken, and their medical history. This allows for the assessment of potential risks and informed decision-making.
Finally, codeine, although widely used for its analgesic and antitussive properties, should therefore be reserved for situations where the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. Each use must be justified, and any patient on this medication must be medically supervised to limit risks.

FAQ on the medical prescription of codeine
Q: What is codeine?
A: Codeine is a substance extracted from the latex of the opium poppy, known for its analgesic and antitussive effects. It works by blocking pain signals in the central nervous system.
Q: What are the side effects of codeine?
A: The most common undesirable effects of codeine include constipation, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and impaired alertness in case of a too high dose.
Q: What are the risks of codeine overdose?
A: An overdose of codeine can lead to impaired alertness and a slowed breathing, potentially leading to respiratory arrest, which may result in death.
Q: Can codeine create dependence?
A: Yes, prolonged use of codeine can lead to a tolerance phenomenon or even dependence. It is crucial to use it only within the framework of a medical prescription.
Q: What are the contraindications of codeine?
A: Codeine is contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity to the molecule, asthma, severe hepatic or renal insufficiency, as well as in patients with respiratory and convulsive disorders.
Q: Is it dangerous to mix codeine with alcohol?
A: Yes, alcohol can increase the effect of codeine, thus enhancing the undesirable effects of both substances and leading to impaired alertness and a risk of respiratory depression.
Q: In what cases is codeine prescribed?
A: Codeine is primarily prescribed to treat moderate acute pain and dry or irritating coughs, when conventional treatments such as paracetamol or ibuprofen are ineffective.