Tiotropium is a medication commonly prescribed for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. As a bronchodilator, it facilitates breathing by relaxing the muscles of the airways. However, like any treatment, tiotropium can lead to undesirable side effects and has certain contraindications. In managing patients suffering from respiratory disorders, it is crucial to assess the risks associated with its use. Side effects can vary in intensity and may include symptoms such as dry mouth, heart palpitations, or gastrointestinal disturbances. The contraindications, on the other hand, depend on the medical profiles of the patients. Therefore, it is essential to conduct a thorough evaluation of the medical history before initiating treatment with tiotropium. This approach helps to better understand how this medication interacts with pre-existing conditions and other treatments. Understanding the risks associated with tiotropium is a key issue in ensuring a safe and effective management for patients.
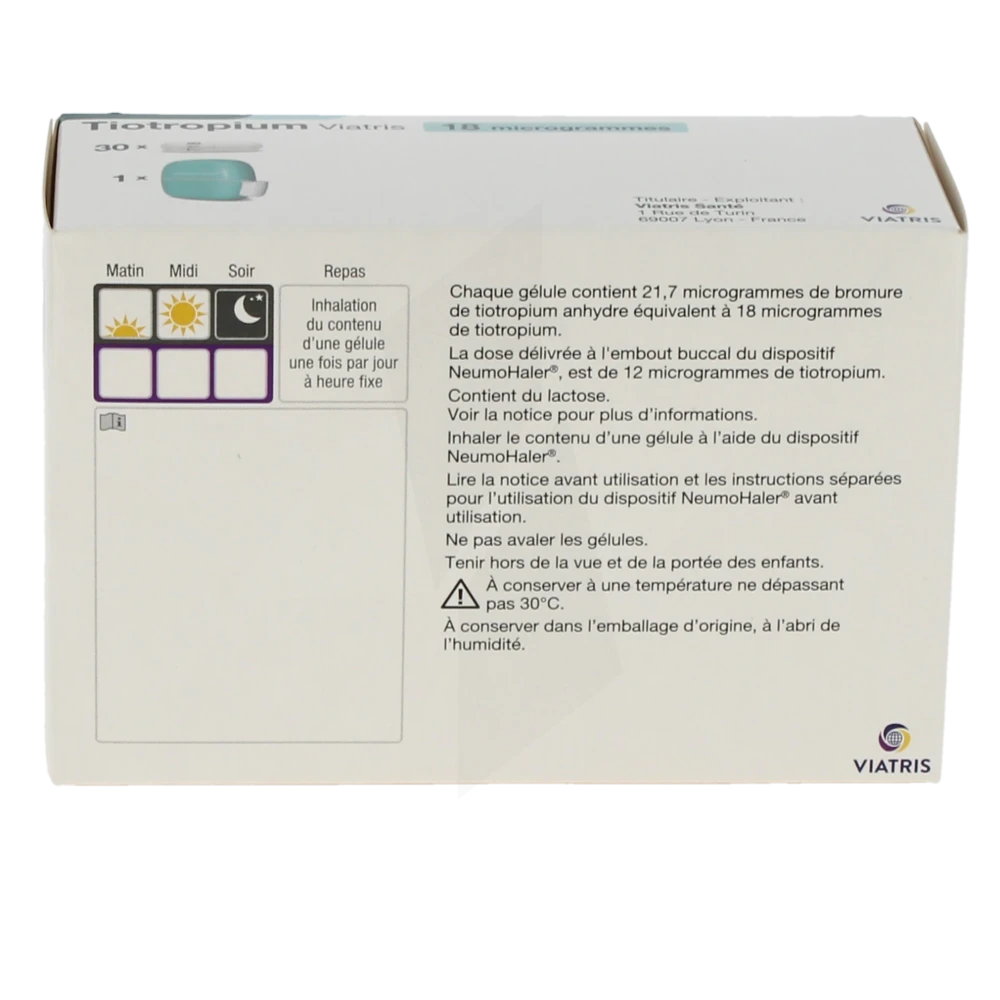
The tiotropium is a medication commonly prescribed for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and severe asthma. It belongs to the class of long-acting anticholinergics. By widening the airways, it allows for better lung ventilation, thereby improving the quality of life for patients. However, like any medication, tiotropium can lead to side effects and presents specific contraindications that must be taken into account.
Side Effects of Tiotropium
The adverse effects of tiotropium can vary from patient to patient. Some patients may experience mild symptoms, while others may face more serious issues. Here are some of the most commonly reported side effects:
- Dry mouth: This symptom can be particularly bothersome, leading to difficulty in speaking or swallowing.
- Constipation: Another reported adverse effect that can also impact overall well-being.
- Allergic reactions: In rare cases, some patients may develop rashes or itching due to an allergic reaction to the medication.
- Cough and irritation: Feelings of throat irritation or coughing may occur, often due to inhalation of the medication.
- Palpitations: Some patients may experience heart palpitations, which require thorough evaluation.
It is essential to monitor these side effects and discuss them with a healthcare professional if these symptoms persist or worsen. Early identification of side effects can facilitate modifications to the treatment if necessary.
Contraindications of Tiotropium
Before starting treatment with tiotropium, it is crucial to carefully assess the patient’s medical history. Certain patients may be at increased risk if the medication is administered under specific conditions. The main contraindications include:
- Hypersensitivity: Individuals who have experienced allergic reactions to tiotropium components or other anticholinergics should not use this medication.
- Closed-angle glaucoma: This type of glaucoma may be exacerbated by the use of anticholinergics.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): Tiotropium may potentially cause complications in patients with BPH, such as urinary retention.
- Cardiac diseases: Patients with a history of heart diseases should exercise caution when using tiotropium, especially if they are already taking other treatments affecting cardiac function.
- Liver or renal insufficiency: Patients with liver or kidney problems should consult their physician to determine the safety of using tiotropium.
Adhering to the contraindications is fundamental to ensure patient safety and maximize the efficacy of treatments. Each patient is unique, and it is imperative to openly discuss medical history and concerns with a qualified healthcare professional.
Precautions to Consider Before Prescribing
Before prescribing tiotropium, it is essential to inform patients of the precautions to take. This includes:
- Assessment of allergies: Verify the absence of known allergies to anticholinergics or specific components of the medication.
- Regular follow-up: Regular consultations should be established to assess the efficacy of tiotropium and manage any potential side effects.
- Patient education: It is important to inform patients on how to properly use the inhalation device to maximize drug absorption.
- Action plan for adverse events: Provide patients with clear instructions on what to do in case of serious or unexpected side effects.
Each therapeutic intervention should be personalized, taking into account individual needs and any existing contraindications in the patient.

FAQ About Tiotropium Prescription: Side Effects and Contraindications
What is tiotropium? Tiotropium is an anticholinergic medication primarily used to treat bronchial fog in cases of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
What are the common side effects of tiotropium? The most frequent side effects include dry mouth, headaches, and gastrointestinal disturbances. It is important to report any adverse effects to a healthcare professional.
Is tiotropium safe for all patients? No, tiotropium may have contraindications for certain patients, particularly those suffering from bronchial issues, glaucoma, or bladder stenosis. Medical advice is always necessary before starting treatment.
How should tiotropium be administered? Tiotropium is generally administered via inhalation. It is crucial to follow the doctor’s instructions and adhere to the inhalation device’s manual.
Are there any drug interactions to consider with tiotropium? Yes, tiotropium may interact with other bronchodilator medications or those with anticholinergic effects. It is essential to communicate to your doctor all medications you are taking.
What signs should alert in case of using tiotropium? If you experience an increase in difficulty breathing, heart palpitations, allergic reactions, or other unusual symptoms, contact a healthcare professional immediately.
Is tiotropium compatible with other treatments? This depends on individual cases. Always discuss with your doctor the ongoing treatments to avoid negative interactions.
Can I use tiotropium if I am pregnant or breastfeeding? It is recommended to consult a physician before using tiotropium during pregnancy or breastfeeding to assess the potential risks and benefits.