Duloxetine is an antidepressant belonging to the class of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Used to treat depression and certain anxiety disorders, it offers numerous benefits. However, its prescription requires particular attention due to potential side effects and contraindications that may arise. A thorough understanding of these aspects is essential to ensure safe and effective use of this medication, in order to prevent undesirable complications for patients.
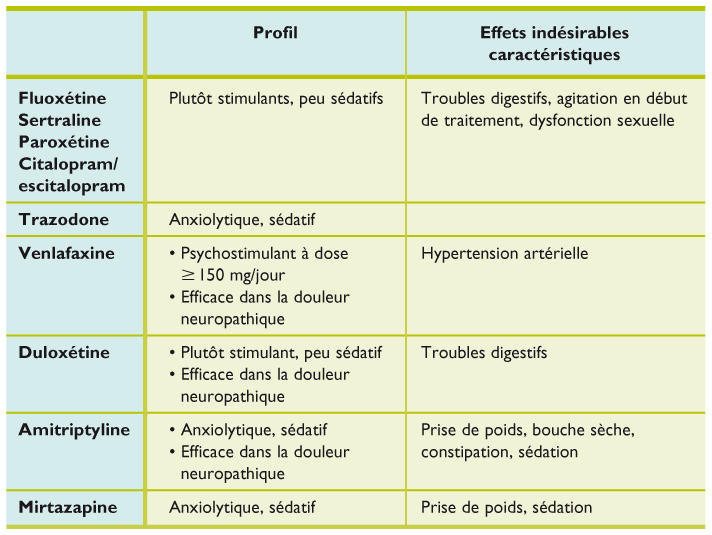
Duloxetine is an antidepressant classified among the serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Its use is common in the treatment of various disorders, including major depression and generalized anxiety, as well as in the management of neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. Understanding the side effects and contraindications related to the prescription of duloxetine is essential to optimize its efficacy while minimizing potential risks.
Side Effects of Duloxetine
Like any medication, duloxetine has side effects that may vary from person to person. These effects should be closely monitored throughout the treatment. Although they do not occur in all patients, being aware of them can aid in appropriate management.
The most common adverse effects associated with duloxetine include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and constipation. In fact, clinical studies show that a percentage of patients receiving duloxetine report these symptoms, especially during the first days of treatment. A correlation has also been observed between the start of treatment and the onset of adverse effects, a delay that can be estimated between two and four weeks before the benefits of the medication are felt.
Other less frequent but serious side effects include hypertension, palpitations, and changes in heart rhythm. It is essential to carry out regular monitoring of blood pressure in patients on duloxetine, especially in those with a history of hypertension.
Neurological effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, or insomnia may also occur. These effects, although transient for most, can affect the quality of life and may require dosage adjustment or reevaluation of the relevance of the treatment. Special attention should also be paid to signs of allergic reactions, although rare, including hives or breathing difficulties.
Contraindications of Duloxetine
Before prescribing duloxetine, it is crucial to consider the contraindications that may limit its use. Caution is advised, particularly in patients with certain medical conditions or taking other medications.
Duloxetine is strictly contraindicated in patients with a history of allergic reaction to any of the components of the medication. It is also strongly advised against combining it with other medications in the monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) class, due to the high risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially fatal condition.
Individuals suffering from liver disorders or severe kidney diseases should have their treatment reevaluated by a healthcare professional. Indeed, the elimination of duloxetine from the body may be compromised, leading to prolonged exposure and increased risks of side effects.
Finally, in patients at high risk for closed-angle glaucoma or those with a history of bipolar disorder, caution is also warranted. It is recommended to consult a physician to discuss the implications of duloxetine treatment and possible alternatives based on symptoms and the patient’s overall health status.
For detailed information on prescriptions and recommendations associated with duloxetine, access to medical resources such as Vidal can be useful. It is also recommended to consult specialized platforms in order to learn about drug interactions and the impact of food on treatment effectiveness.
In a practical context, educating patients about the expected and potential side effects of duloxetine can enhance treatment compliance. This information plays a central role in establishing a trusting relationship between doctor and patient, thus facilitating regular follow-up and necessary treatment adjustments.

FAQ about Duloxetine
Q: What is duloxetine?
A: Duloxetine is an antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorders and fibromyalgia.
Q: What are the main side effects of duloxetine?
A: Common side effects may include nausea, dizziness, drowsiness, and constipation.
Q: Does duloxetine have contraindications?
A: Yes, duloxetine is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe allergic reactions to this medication or to other serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.
Q: How long does it take for duloxetine to work?
A: The effectiveness of duloxetine is generally not immediate; a period of 2 to 4 weeks is often necessary to feel beneficial effects.
Q: What are the risks of mixing duloxetine with other medications?
A: It is important to avoid mixing duloxetine with certain other medications, particularly other antidepressants, as this can increase the risk of severe adverse effects.
Q: What should I do if I experience side effects?
A: If you experience adverse effects, it is essential to consult your doctor for an assessment and, if necessary, an adjustment of treatment.
Q: Can duloxetine have food interactions?
A: Yes, certain foods, particularly citrus fruits, can interact with duloxetine and affect its effectiveness.
Q: What is the best time to take duloxetine?
A: Duloxetine can be taken either in the morning or in the evening, but it is advisable to follow the recommendations of the treating physician.