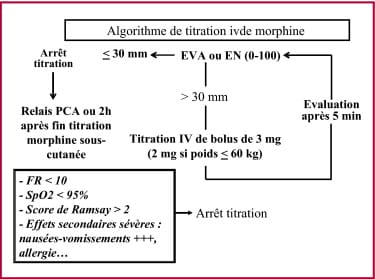
The medical prescription of morphine requires special attention due to its powerful effects and associated risks. Primarily used to relieve severe pain, this treatment can cause various side effects such as drowsiness, nausea, and constipation, and may have contraindications for certain populations. A good understanding of these elements is essential to ensure adequate care for patients, thereby minimizing the risks of dependence or adverse effects.
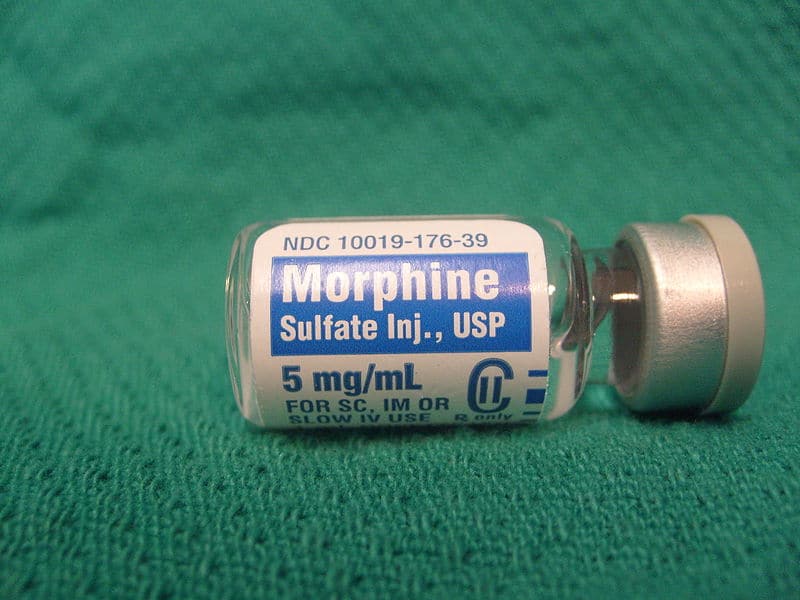
Morphine is a powerful opioid analgesic primarily prescribed for the treatment of moderate to severe pain. Used in a medical setting, its use requires a deep understanding not only of its indications but also of its side effects and contraindications. This article aims to explore these essential aspects to ensure effective and safe prescribing.
The side effects of morphine
The side effects of morphine can vary from person to person, often influenced by dosage, duration of treatment, and individual patient sensitivity. While they do not affect all users, it is crucial to be aware of them.
Common adverse effects include:
- Drowsiness: One of the main side effects that can affect alertness, requiring caution in activities such as driving or operating machinery.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Common manifestations that may require the prescription of other medications to alleviate them.
- Constipation: Common in long-term therapy, it may require preventive measures such as increasing fiber and fluid intake.
- Dizziness: These feelings of discomfort may occur, especially during the initial doses.
- Dry mouth: This symptom can be unpleasant, but solutions exist to relieve it.
- Depressed respiration: A serious effect that requires increased monitoring.
In addition to these effects, other reactions may manifest, requiring a comprehensive analysis of each patient. Note that severe cases of allergies may also occur, characterized by itching or skin rashes. In a clinical setting, particular attention should be paid to warning signs.
Contraindications to morphine prescription
Morphine is subject to use restrictions, and certain contraindications must be absolutely respected to avoid serious complications.
The main contraindications include:
- Allergies: Anyone known to have a hypersensitivity to morphine or any of its excipients should not be treated with this medication.
- Decompensated respiratory failure: Morphine can worsen respiration, making its use inappropriate in these cases.
- Severe asthma and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease): The use of morphine can cause respiratory complications.
- Head injuries: Due to its potential to reduce alertness, morphine is not recommended for patients who have suffered head injuries.
- Uncontrolled epilepsy: Unstable epileptic patients should not be treated with morphine.
- Intracranial hypertension: This condition could be exacerbated by the use of the medication.
It is essential to discuss each patient’s medical history before starting treatment with morphine. Indeed, early identification of contraindications helps ensure patient safety and optimize the overall effectiveness of pain relief therapy.
Management of side effects and medical follow-up
The management of side effects of morphine relies on effective communication between the patient and the healthcare professional. Any unpleasant manifestation should be reported promptly to adjust treatment if necessary. Here are some joint recommendations:
- Increase fiber and fluid intake to prevent constipation.
- Assess the need for anti-nausea medications to minimize nausea.
- Monitor respiration at each consultation, particularly for patients with respiratory histories.
Moreover, it is advisable to carry out regular assessments to adjust dosage based on the patient’s response and potential signs of dependence. Patients should be informed of the risks associated with a sudden stop of morphine, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
It is worth noting that pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss the necessity of treatment with their doctor, as the use of morphine can have consequences for embryonic or neonatal development.
In conclusion, although morphine is an effective treatment for severe pain, it requires special attention. For more information regarding all the specifics of morphine, you can consult resources such as the Public Database of Medicines or the direct medicine advice. In-depth studies of level 3 analgesics also provide an enriching perspective.
It is always advisable to refer to practical guides such as those provided by the University Hospitals of Geneva and other positions on the use of morphine in modern pharmacology for a safe and informed approach.

FAQ on morphine: side effects and contraindications
Q : What are the common side effects of morphine?
A : Common side effects include drowsiness, nausea, constipation, and dizziness. Other effects may occur such as dry mouth, fainting, or itching.
Q : Can morphine cause addiction?
A : Yes, taking morphine over an extended period can lead to addiction. Therefore, it is recommended not to stop the treatment abruptly without medical advice.
Q : Who should not take morphine?
A : Morphine is contraindicated for individuals with decompensated respiratory failure, seriously controlled disorders, intracranial hypertension, or intestinal obstruction, among others.
Q : Is morphine safe during pregnancy?
A : Morphine is generally discouraged during pregnancy and its use should be carefully evaluated by a doctor.
Q : What to do in case of concerning side effects?
A : It is important to report any suspected side effects to your doctor or pharmacist, especially if they worsen.
Q : Is it safe to drink alcohol while taking morphine?
A : No, it is not recommended to drink alcohol at the same time as morphine, as this can worsen sedative effects.
Q : How should you take morphine?
A : Morphine can be taken orally in the form of tablets, capsules, or liquid, or administered intravenously. It is essential to follow the doctor’s instructions.