Fentanyl is a powerful analgesic classified among opioids, widely used in the treatment of chronic pain, especially in medical settings. However, its use is not without risks. Indeed, the side effects can be numerous and sometimes serious, ranging from drowsiness and nausea to more severe complications such as respiratory depression. Furthermore, specific contraindications must be adhered to in order to prevent potentially fatal adverse reactions. A thorough understanding of the implications of its prescription is therefore essential to ensure patient safety.

Fentanyl is a powerful opioid primarily used for the treatment of intense and chronic pain, particularly in palliative care or in the management of post-surgical pain. Due to its high analgesic efficacy, it is classified as a narcotic medication, subject to strict regulations. Understanding the potential side effects as well as the contraindications of fentanyl is crucial to ensure its safe and effective use in a medical context.
Side effects of fentanyl
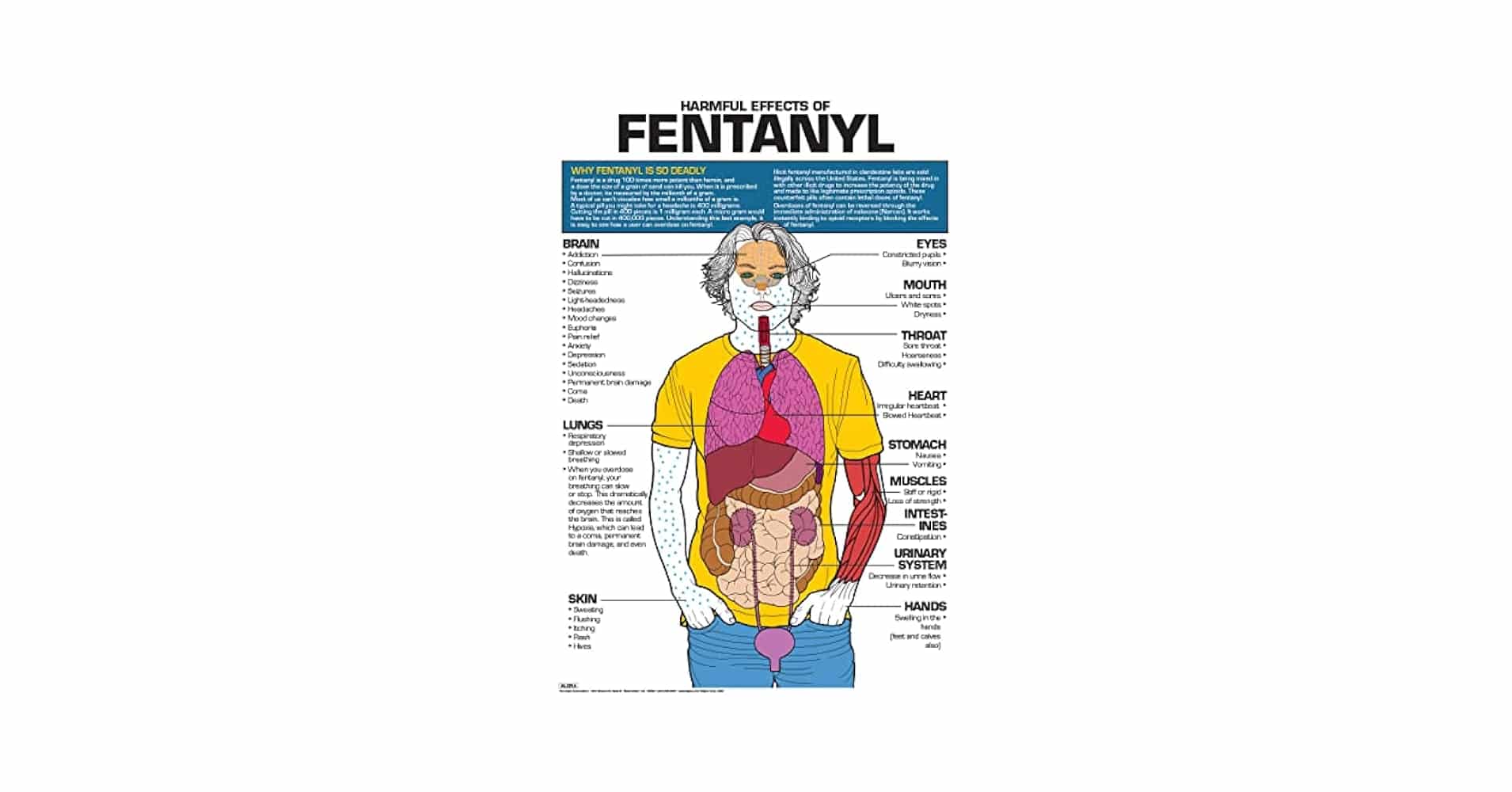
Fentanyl, although primarily prescribed for its analgesic properties, can lead to a range of undesirable effects in patients. These effects vary depending on the administered dose, the route of administration, and the individual sensitivity of the patient. It is essential for doctors to properly inform patients of the risks associated with this medication and to perform careful follow-up.
The most commonly reported side effects include:
- Nausea: Many fentanyl users experience feelings of nausea, which may also be accompanied by vomiting. This can be particularly unpleasant for patients already weakened by their condition.
- Constipation: One notable drawback of opioids is their tendency to cause constipation. Fentanyl can slow down intestinal transit, leading to additional discomfort.
- Drowsiness: Patients may experience significant fatigue or excessive drowsiness, which can interfere with their daily activities and quality of life.
- Dizziness: The sensation of dizziness is also common, and in some cases, it can increase the risk of falls, especially in older adults.
- Respiratory difficulties: Opioids like fentanyl can affect breathing, slowing the respiratory rate and causing difficulties for some patients, particularly those with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
It is also important to note that some side effects, although less frequent, can be extremely serious, including:
- Hypersensitivity: Some individuals may develop allergic reactions to fentanyl, such as skin rashes or edema, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Loss of appetite or anorexia: Changes in appetite may occur, affecting the patient’s nutrition.
- Mental state changes: Mood disorders, including depression or anxiety, may manifest in some patients, necessitating thorough examination.
- Overdose: Excessive use of fentanyl can lead to critical situations, with symptoms such as respiratory depression, loss of consciousness, and, in extreme cases, death.
Contraindications for the use of fentanyl
Before prescribing fentanyl, it is essential for the physician to carefully assess the patient’s medical history. Several contraindications must be considered to prevent serious complications. Here is an overview of the main contraindications for the use of fentanyl:
- Allergies to fentanyl or its excipients: Patients with a known hypersensitivity to fentanyl should avoid using this medication, as even low doses can trigger a severe reaction.
- Respiratory depression: Fentanyl is strictly contraindicated in patients suffering from severe respiratory depression or an obstructive pulmonary disease, as its use can exacerbate these conditions and compromise respiratory function.
- Absence of background morphine treatment: In some cases, prescribing fentanyl is inappropriate if the patient is not already on background morphine treatment, thereby increasing the risk of respiratory depression.
- Cardiac pathologies: Patients with a history of heart problems, such as palpitations or cardiac arrest, should be subjected to particularly rigorous evaluation before fentanyl prescription, as the use of opioids could lead to myocardial complications.
- Use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): Patients taking MAOI medications should refrain from using fentanyl, as this could increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, leading to potentially fatal reactions.
- Children under two years old: Fentanyl is considered too potent for very young children; any prescription must be carefully evaluated and justified by a physician.
It is also essential to maintain open communication between the physician and the patient regarding the proper use of fentanyl, as well as to ensure the patient is aware of the risks associated with this type of medication.
Due to its efficacy but also its risks, fentanyl must be prescribed with caution. Careful monitoring of side effects and a thorough understanding of the contraindications will optimize the therapeutic experience for patients while minimizing associated risks. Healthcare professionals must commit to providing clear information to patients and closely monitoring their health status when initiating treatment with this opioid. For more information on fentanyl, readers can refer to resources such as the official ANSM site, or Vidal for informative sheets.
FAQ: Medical prescription, side effects, and contraindications of fentanyl
Q: What are the side effects of fentanyl?
A: The side effects of fentanyl may include nausea, constipation, drowsiness, dizziness, headaches, and respiratory difficulties. Other less frequent effects may include loss of appetite, psychiatric disorders, and taste changes.
Q: Are there any contraindications for the use of fentanyl?
A: Yes, fentanyl by buccal route is contraindicated in cases of allergy to fentanyl, in the absence of background morphine treatment, and in situations of severe respiratory depression or severe obstructive pulmonary disease.
Q: Why does fentanyl require a medical prescription?
A: Fentanyl is a narcotic, and its prescription is regulated due to the risks associated with its use, particularly dependence and the risk of overdose.
Q: What types of adverse effects should be monitored during the use of fentanyl?
A: Signs to watch for include respiratory depression, hypotension, and excessive drowsiness, which may indicate a potential overdose of the medication.
Q: What precautions should be taken when using fentanyl?
A: It is crucial to inform your doctor of any pre-existing medical conditions, the use of other medications, and to closely observe withdrawal symptoms if the use of fentanyl needs to be discontinued.