In the field of modern medicine, the prevention of blood clots is a major issue. Among the available treatments, apixaban, marketed under the name ELIQUIS, stands out for its effectiveness. Prescribed to reduce the risk of clot formation, this medication plays a crucial role in managing venous thromboembolic disorders. However, the use of apixaban requires special attention due to its potential side effects. These effects include, for example, the occurrence of bleeding, which is the most frequently observed adverse effect. Patients may also experience allergic reactions or hypersensitivity to the medication, making medical monitoring all the more critical. In this introduction, we will explore the main indications of apixaban, as well as the precautions to take when prescribing it. We will also discuss recommendations regarding diet and drug interactions, to ensure optimal management and avoid undesirable complications.
Apixaban, marketed under the name ELIQUIS, is an oral anticoagulant that plays an essential role in the prevention and treatment of thrombosis. Primarily used to reduce the risk of blood clot formation, this medication specifically blocks Factor Xa, a key enzyme in the blood coagulation process. Its use is particularly common among patients who have undergone orthopedic surgery or those suffering from certain heart diseases.
In terms of its effectiveness, the prescription of apixaban involves rigorous medication monitoring. As a physician, it is critical to discuss the benefits, but also the associated risks of this treatment. Although apixaban is generally well tolerated, it is not without adverse effects. Therefore, it is paramount for patients to be informed about the manifestations that may occur during its administration.
The indications of apixaban and its mechanism of action
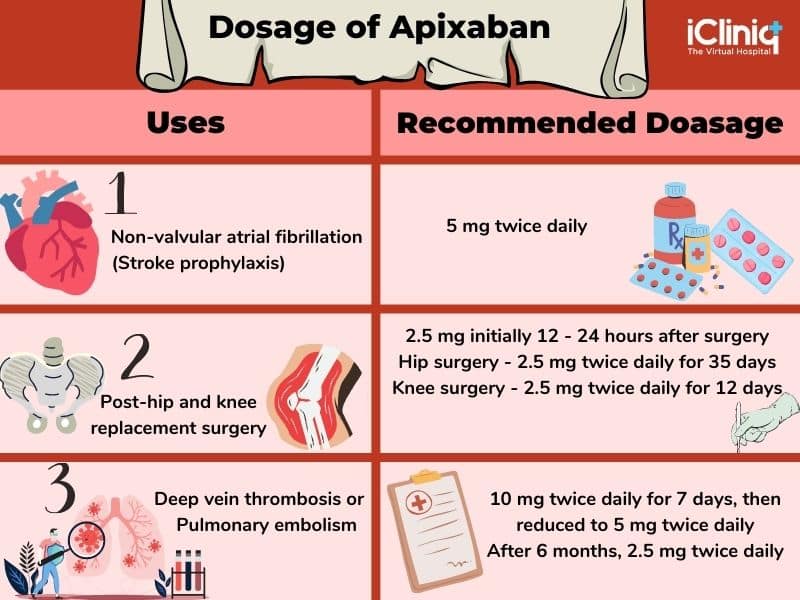
Apixaban is indicated for several conditions, notably the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults who have undergone surgical procedures, as well as for reducing the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. By blocking Factor Xa, apixaban prevents the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, thereby decreasing fibrin formation and inhibiting the coagulation process. This results in a significant reduction in the risk of clot formation.
Regarding dosage, apixaban is administered with dosing regimens tailored to the individual needs of each patient. Generally, 5 mg is the standard dose, which can be adjusted based on factors such as weight, age, and renal function. It is crucial that patients strictly follow their prescription to avoid any complications associated with underdosing or overdosing.
Side effects of apixaban: watch for distress signals
Despite its recognized effectiveness, apixaban can cause side effects. The most common adverse effects associated with this medication are primarily related to its anticoagulant action, with the occurrence of bleeding being the most reported complication. Patients should be particularly vigilant in cases of bleeding gums, rectal bleeding, or blurry vision, which may indicate an eye hemorrhage.
It is also recommended to immediately report any allergic swelling or anaphylactic reaction, which, although rare, may occur in certain individuals. Signs such as itching, facial swelling, breathing difficulties, or a skin rash should be taken seriously.
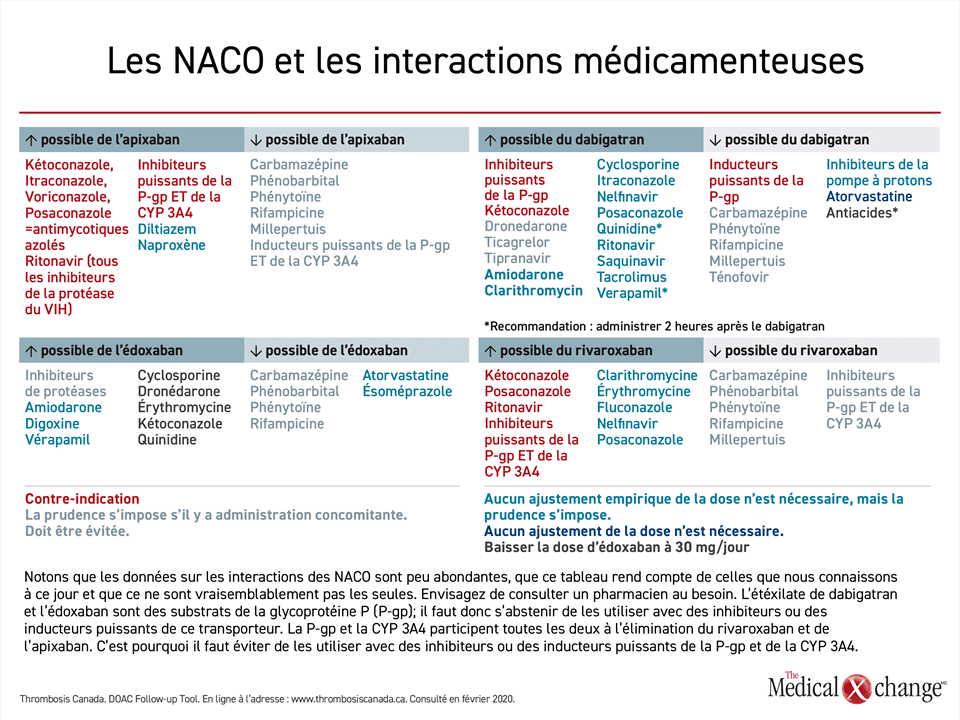
Patients taking apixaban should also be aware of potential drug interactions that could enhance side effects. Indeed, certain medications, vitamins, or dietary supplements may increase the risk of bleeding or deactivate the anticoagulant effect. A thorough evaluation of concomitant medications is therefore essential to ensure the safety of the treatment.
Information regarding apixaban and its side effects is available in official documents, such as the patient information leaflet and various prescription guides. These documents provide clear instructions on how to manage side effects and offer necessary precautions before beginning treatment.
For any questions regarding possible side effects and the use of apixaban, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or refer to reliable documentation sources, such as the Global Santé website.