Fluoxetine is a widely used medication in the treatment of various psychological disorders, including depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and binge eating disorder. Prescribed for its ability to improve mood by acting on serotonin, it is often considered an effective therapeutic choice. However, understanding its side effects is essential to optimize its use and ensure patient safety. Manifestations such as nausea, insomnia, and headaches may occur, highlighting the importance of careful monitoring throughout treatment. This presentation aims to provide an overview of the key aspects related to the medical prescription of fluoxetine, as well as the associated side effects.

Fluoxetine, commonly known under the name Prozac, is a widely prescribed psychotropic medication. Classified among the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), it is primarily used to treat depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders, binge eating episodes, and certain anxiety disorders. Its prescription is carried out under the strict supervision of a healthcare professional, as a long-term or short-term treatment.
Therapeutic indications of fluoxetine
Fluoxetine is generally prescribed in several clinical situations. Its main indication remains the treatment of major depressive episodes in adults. This medication is also used in the management of obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD), a condition characterized by unwanted intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors. In conjunction with psychotherapy, fluoxetine can reduce the frequency of binge eating episodes, allowing for better control of eating behavior.
It should be noted that fluoxetine may also be used in certain situations for adolescents, particularly for the treatment of depression and OCD, always under rigorous medical supervision. Before starting treatment, the physician will carefully evaluate the patient’s medical history, mental health background, and any presence of other medical conditions that may interact with the medication.
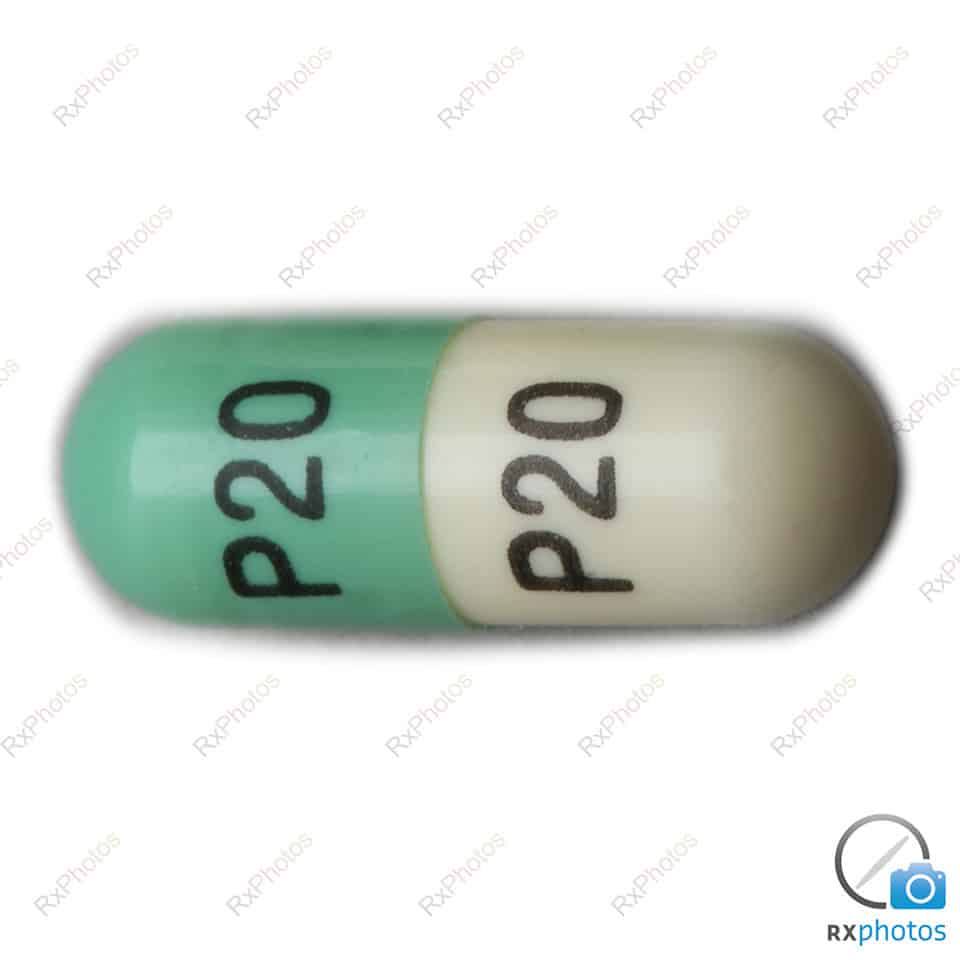
Dosing and administration of fluoxetine
The initial dosage of fluoxetine is generally 20 mg per day, administered in capsule form. This dosage can be adjusted by the physician based on the patient’s clinical response. If symptoms persist, the treatment may be gradually increased to doses of up to 60 mg per day, but this change must be supervised by a physician to minimize side effects.
It is crucial to inform the patient about the administration modalities of fluoxetine. In fact, it is advised to take this medication in the morning to avoid potential sleep disturbances. In case of a missed dose, it is recommended to take it as soon as possible unless it is close to the time for the next dose. In this case, skip the missed dose without doubling the next dose.
Side effects of fluoxetine
Like all medications, fluoxetine can lead to side effects, some being more common than others. Among the frequently reported side effects, we find:
- Nausea: A feeling of discomfort which may be accompanied by vomiting.
- Insomnia: Difficulties falling asleep or maintaining sleep throughout the night.
- Headaches: Pain that can vary in intensity, ranging from mild to severe.
- Loss of appetite: In some cases, patients may notice a decrease in the desire to eat.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of weakness or lack of energy may be present.
In less frequent cases, more severe effects may occur. It is essential that anyone taking fluoxetine consults their physician in case of unusual or concerning symptoms, such as severe agitation, suicidal thoughts, or signs of allergies.
It is also important to emphasize that fluoxetine can interact with other medications, including other antidepressants or anticoagulants. Open communication with the physician about all ongoing treatments is crucial to ensure the patient’s safety.
Risk of dependence and withdrawal
Unlike some other types of antidepressants, fluoxetine presents a relatively low risk of physical dependence. However, sudden withdrawal can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, mood disturbances, or sensations of electric shock. Thus, the process of stopping should be done gradually, under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Increasingly, studies question physicians on the necessity of reevaluating the continuation of certain antidepressant treatments over extended periods. Although fluoxetine is generally well tolerated, it is essential to weigh the risk of accumulated side effects against the therapeutic benefits obtained.
Fluoxetine is an effective medication for treating various mental disorders. Its prescription must be carried out by a qualified healthcare professional, who will consider the specifics of each patient. Knowing that side effects are possible, regular monitoring is of utmost importance to ensure the treatment proceeds well. To deepen your knowledge about this medication, it is recommended to consult available medical resources and ask questions during consultations.
For more details about fluoxetine, consult the following links: Practical guide to fluoxetine, Fluoxetine 20 mg, Medications and memory, Questions about antidepressants, Fluoxetine medication sheet.
FAQ about fluoxetine: Medical prescription and side effects
Q : What is fluoxetine?
A : Fluoxetine is an antidepressant that belongs to the class of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It is used to treat various disorders, including depressive episodes and obsessive-compulsive disorders.
Q : In what cases is fluoxetine prescribed?
A : Fluoxetine is prescribed to treat conditions such as depressive episodes, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and binge eating disorder, usually in conjunction with psychotherapy.
Q : What is the recommended dosage for fluoxetine?
A : The recommended initial dosage is 20 mg per day. If there is insufficient response after two weeks, a gradual increase up to 60 mg per day may be considered.
Q : What are the common side effects of fluoxetine?
A : Common side effects include nausea, headaches, sleep difficulties (insomnia), and loss of appetite. Other effects may also manifest, such as nervousness and sexual problems.
Q : What should I do if I experience side effects?
A : It is essential to report any side effects to your doctor. They can provide appropriate advice and adjust your treatment if necessary.
Q : Are there risks associated with the use of fluoxetine?
A : Like any medication, fluoxetine may carry risks of adverse effects. Some individuals may also experience difficulties when withdrawing after prolonged treatment.
Q : Can fluoxetine interact with other medications?
A : Yes, fluoxetine can interact with certain medications. It is important to discuss with your doctor all medications, including over-the-counter medications, that you are taking before starting treatment with fluoxetine.