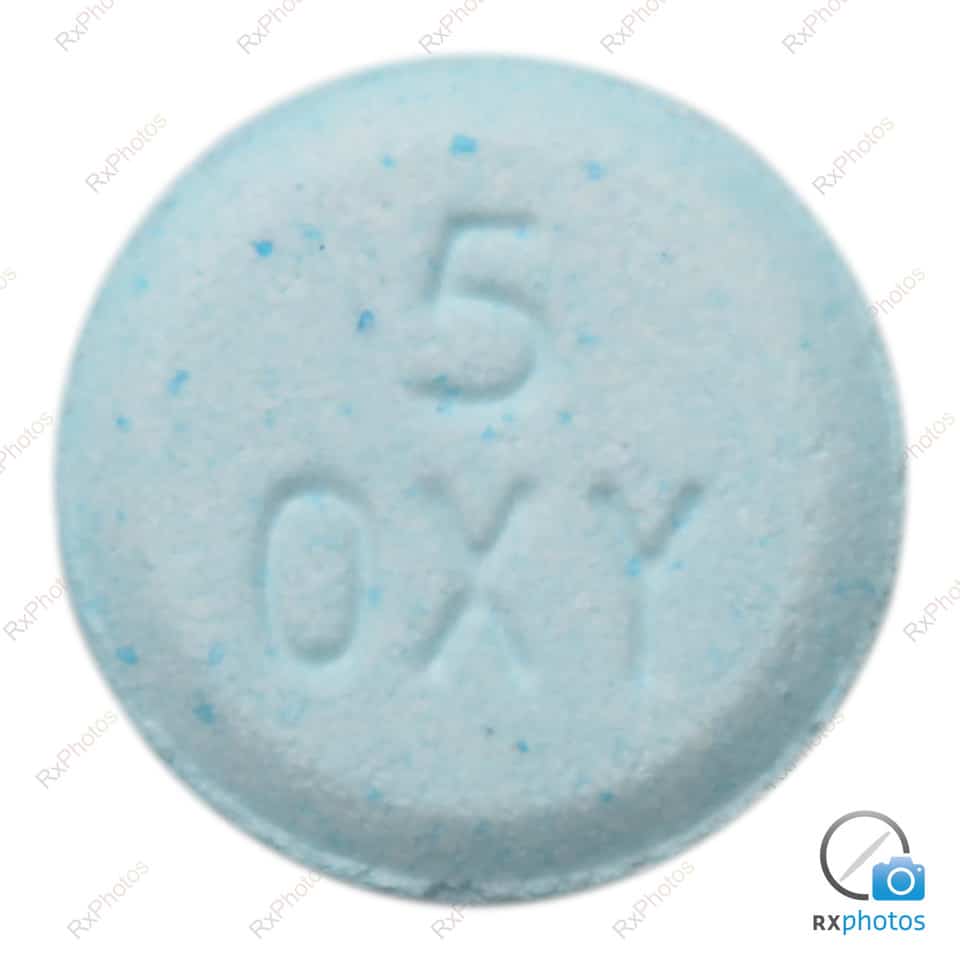
The medical prescription of oxycodone, a powerful analgesic, requires particular attention due to its potential side effects and contraindications. Primarily used to treat moderate to severe pain, this medication can lead to various adverse reactions, ranging from constipation to more serious effects such as respiratory disorders. Furthermore, certain medical conditions make its use risky, requiring thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional before any prescription. A clear understanding of these issues is essential to optimize treatment while ensuring patient safety.
Oxycodone is an opioid medication often used to treat moderate to severe pain, particularly after surgery or in the case of chronic illnesses. Although it is effective in relieving pain, oxycodone also presents a number of side effects and contraindications that require careful consideration when prescribing. This in-depth analysis focuses on these crucial aspects.
Side effects of oxycodone
Like any medication, oxycodone causes adverse effects that can vary depending on dosages, the duration of treatment, and the individual sensitivity of the patient. The side effects can be classified according to their frequency of occurrence, ranging from the most common to the least common.
The most frequently reported adverse effects include:
- Constipation: This effect is notorious among patients on opioids, as the medication slows intestinal transit.
- Drowsiness: Drowsiness is often reported, especially at the beginning of treatment or when dosage is increased.
- Nausea and vomiting: Although these symptoms may decrease over time, they can be particularly bothersome for the patient.
- Respiratory difficulties: Respiratory depression can occur, which can be dangerous, especially at high doses.
- Headaches and dizziness: Some patients experience feelings of dizziness or headaches.
Other more serious side effects, although less frequent, may occur:
- Allergic reactions: This may manifest as skin rashes or hives.
- Agitation and mood disorders: Increased anxiety or early signs of depression may be noticed.
- Hallucinations: Especially in elderly patients, some individuals may experience misperceptions.
Adverse consequences can harm the overall well-being of the patient, prompting careful monitoring and dosage adjustments. Regular medical follow-up is essential to navigate these inconveniences.
Contraindications to the use of oxycodone
Before prescribing oxycodone, it is imperative to know the situations in which this medication may be contraindicated. Contraindications are crucial aspects of prescription, taking into account pre-existing medical conditions and possible drug interactions.
The main contraindications include:
- Allergies: A history of allergy to oxycodone or other components of the drug would prohibit its use.
- Severe respiratory conditions: Patients suffering from lung diseases such as COPD should avoid this treatment due to the increased risk of respiratory depression.
- Severe bronchial asthma: Since oxycodone can worsen asthma, its use is not recommended.
- Severe liver or kidney failure: Patients with impaired liver or kidney function should avoid oxycodone, as it may lead to drug accumulation in the body.
- Conditions associated with intestinal obstruction: People suffering from paralytic ileus syndrome or other bowel dysfunctions should not receive this treatment.
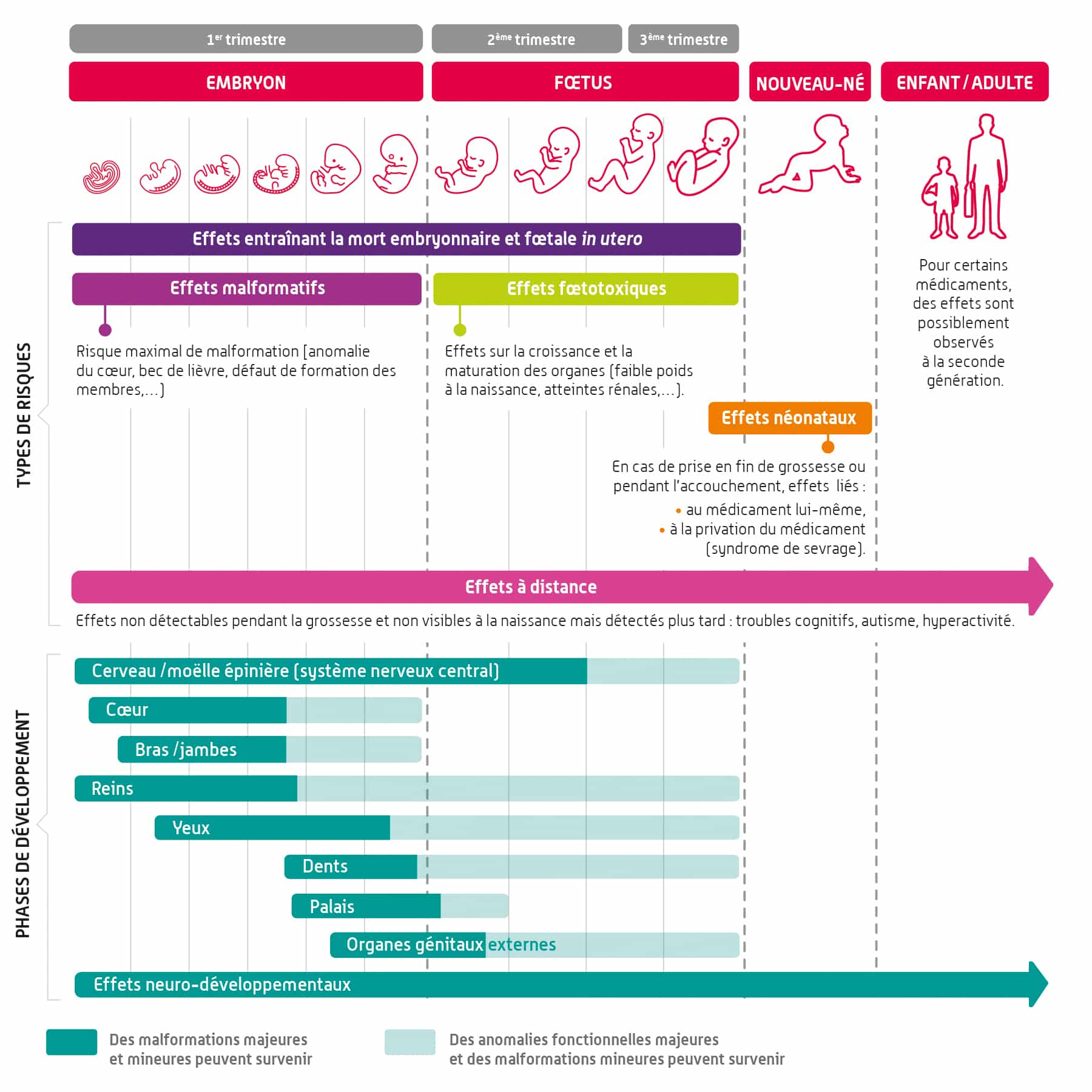
Pregnant women should also be cautious, as adverse effects on the fetus have been observed. Moreover, breastfeeding is an important contraindication, as oxycodone can pass into breast milk and affect the infant.
It is essential to inform patients about these contraindications and to consider their medical history before any prescription. An open dialogue between the doctor and the patient allows for optimizing treatment and preventing undesirable complications.
Additional precautions when prescribing oxycodone
Beyond direct contraindications, doctors also have the responsibility to pay attention to other factors that could influence the safety of treatment with oxycodone. Interaction with other medications, history of opioid addiction, and underlying medical conditions must be examined thoroughly.
Indeed, taking other sedatives or antidepressants can exacerbate the side effects of oxycodone, increasing the risk of respiratory depression or other complications. Thus, it is wise to regularly review the medication prescribed to a patient.
In summary, the prescription of oxycodone should not be taken lightly. Although it is a valuable ally in the fight against pain, notable side effects and severe contraindications can compromise patients’ health. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment of risks and benefits, coupled with clear communication between the patient and physician, is essential to ensure the safety of treatment.
FAQ on medical prescription: side effects and contraindications of oxycodone
A : The main side effects of oxycodone include constipation, drowsiness, nausea, dizziness, headaches, and respiratory difficulties.
Q : Does oxycodone have rare side effects ?
A : Yes, rare side effects may include bradycardia, hypotension, and itchy rashes.
Q : What are the contraindications of oxycodone ?
A : Contraindications include an allergy to the active ingredient, severe lung diseases, severe bronchial asthma, and severe respiratory depression.
Q : Is oxycodone safe to use during pregnancy ?
A : No, this medication is not recommended during pregnancy and is contraindicated during breastfeeding.
Q : What symptoms may indicate withdrawal syndrome with oxycodone ?
A : Withdrawal symptoms may include anxiety, insomnia, chills, tremors, and nausea.
Q : Are there medications similar to oxycodone ?
A : Yes, similar medications include Actiskenan, Skenan, and Oxycontin.