The medical prescription, a central pillar of public health, requires particular attention to the treatments administered. Among the commonly prescribed medications, fluticasone propionate, often combined with salmeterol, plays a significant role in the treatment of respiratory conditions, particularly allergies. As a corticosteroid, this medication is effective in reducing inflammation and relieving symptoms related to allergic rhinitis or asthma. However, like any treatment, it is accompanied by a range of side effects and contraindications that must be scrupulously considered.
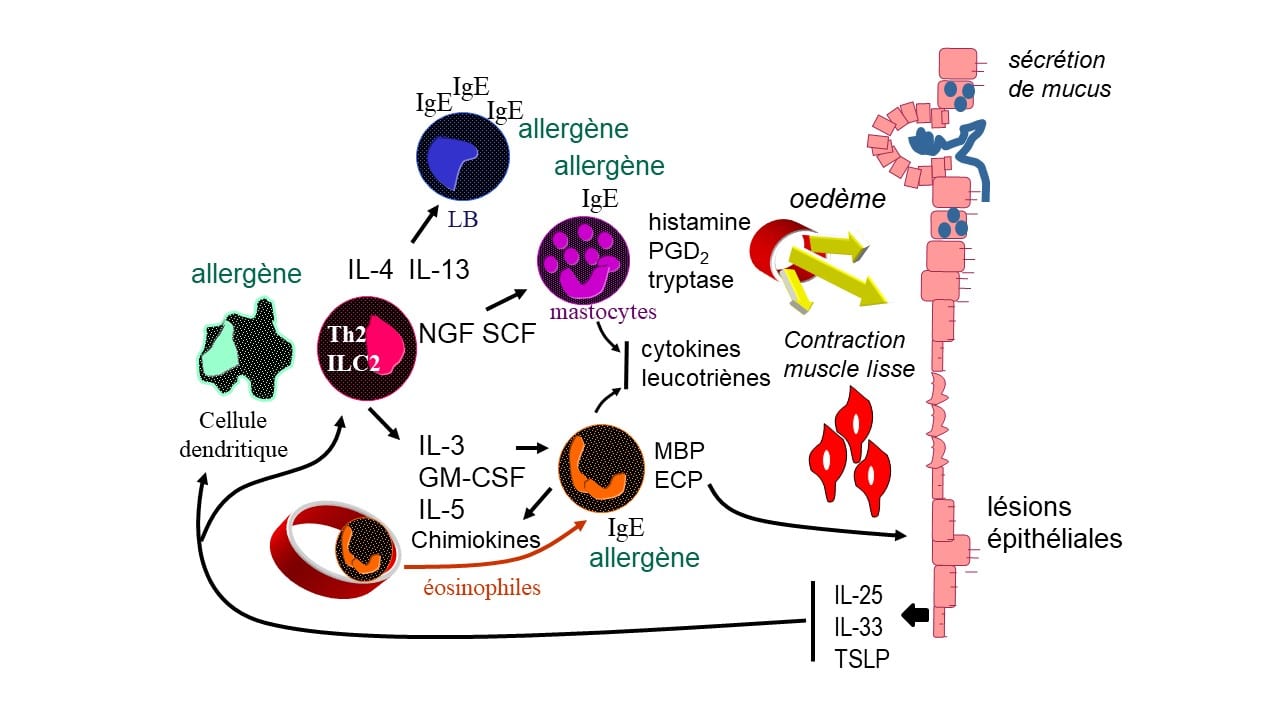
Among the most frequently reported adverse effects are discomforts such as throat irritation, an unpleasant taste sensation, and episodes of epistaxis. More concerning, effects such as depression and aggressiveness may also occur, particularly in children. The risk of developing eye conditions, such as glaucoma, is another alarming aspect to take into account. This analysis of the side effects and contraindications of fluticasone propionate aims to raise awareness about the importance of careful monitoring during its prescription.
Medical Prescription: Side Effects and Contraindications of Fluticasone
Fluticasone propionate is a corticosteroid widely used in the treatment of various respiratory and allergic conditions. This medication is frequently prescribed to patients suffering from allergic rhinitis, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Despite its effectiveness, it is crucial to understand the potential side effects and contraindications associated with this active substance to ensure safe and effective use.
The Side Effects of Fluticasone Propionate
The adverse effects related to the use of fluticasone can vary from person to person and often depend on the route of administration, dosage, and duration of treatment. Among the most common adverse effects are symptoms such as hoarseness, throat irritation, and epistaxis (nosebleeds). These symptoms can be uncomfortable, but they are usually short-lived.
Less common but more concerning effects may also occur. These include oral candidiasis, also known as thrush, which is characterized by white lesions in the mouth. This clinical picture is often observed in patients using inhaled corticosteroids, as prolonged use of these medications may disrupt the local bacterial flora balance.
Additionally, some patients may experience an unpleasant taste sensation or changes in their sense of smell. In rarer cases, treatment with fluticasone has been associated with psychological symptoms such as depression or aggressive behavior, particularly in pediatric populations. It is essential to monitor these signs and discuss them with a healthcare professional if necessary.
Contraindications to the Use of Fluticasone
Before prescribing fluticasone, several contraindications must be taken into consideration. Indeed, this medication is strongly discouraged for patients with a known hypersensitivity to fluticasone or any of the excipients contained in the formulation. Moreover, patients with an active respiratory infection, particularly tuberculosis, should avoid using fluticasone, as it could exacerbate their condition.
History of eye diseases such as glaucoma or cataracts may also present a contraindication to its use, especially in cases of prolonged use. Corticosteroids can indeed increase the risks associated with these eye conditions. Patients suffering from endocrine disorders, such as adrenal dysfunction, must also be carefully evaluated before starting treatment with fluticasone.
Finally, special attention should be paid to children, as the psychological effects mentioned earlier may manifest more prominently in them. It is recommended to assess their behavior before and during treatment to minimize any potential risk.
For more information on the side effects and contraindications of fluticasone, resources such as Ratio-Fluticasone, the ANSM, or Journal des Femmes can be consulted.
It is essential to adequately inform patients about the side effects and contraindications of fluticasone propionate to promote safe use. Special attention should be given to monitoring undesirable symptoms, considering medical history, and evaluating psychological impact, particularly in children. Furthermore, regular follow-up with the healthcare professional will allow for treatment adjustments if necessary to ensure the patient’s well-being.