Dexamethasone, a synthetic corticosteroid, is widely used for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties in various medical treatments. However, its use requires special attention due to its potentially serious side effects and strict contraindications. In the context of prescribing, factors such as the patient’s medical history and existing pathologies must be carefully evaluated to minimize associated risks.
Dexamethasone is often employed in clinical situations where a rapid and effective response is necessary, particularly in certain inflammatory conditions, severe allergies, or in the treatment of certain forms of cancer. However, adverse events such as hyperglycemia, excessive weight gain, and an increased risk of infection may occur, especially with prolonged use. Additionally, certain conditions such as infectious arthritis or viral hepatitis are absolute contraindications to its administration. The importance of a thorough evaluation before prescribing cannot be underestimated, as it is essential to ensure patient safety.
Dexamethasone is a widely used synthetic corticosteroid in medicine for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It is involved in the treatment of various pathologies, including allergic conditions, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancers. However, its use is not without risks, as it can lead to significant adverse effects and has several contraindications that must be considered before starting treatment.
Side Effects of Dexamethasone
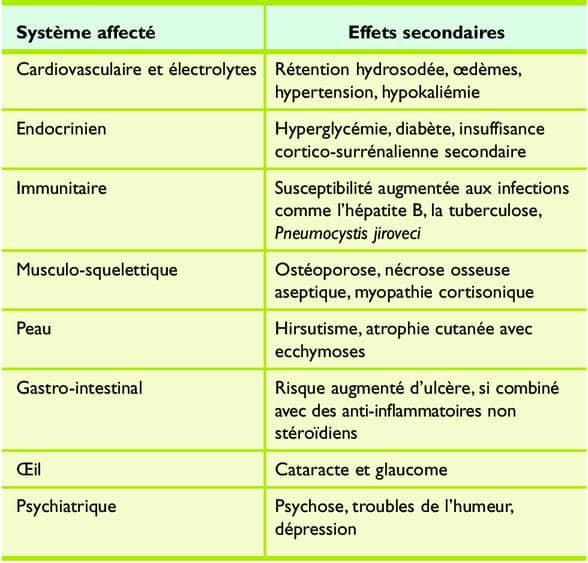
The side effects of dexamethasone can vary from person to person and often depend on the dose administered as well as the duration of treatment. Among the most common adverse effects, symptoms such as:
- Weight gain: Winter may be associated with weight gain due to water retention and fat accumulation.
- High blood pressure: This medication may cause an increase in blood pressure, making medical monitoring necessary.
- Hyperglycemia: Dexamethasone can affect glucose metabolism, leading to high blood sugar levels, particularly in diabetic patients.
- Infections: Due to the immunosuppressive effect of corticosteroids, there is a high risk of infections.
- Digestive problems: Issues such as abdominal pain or ulcers may also occur.
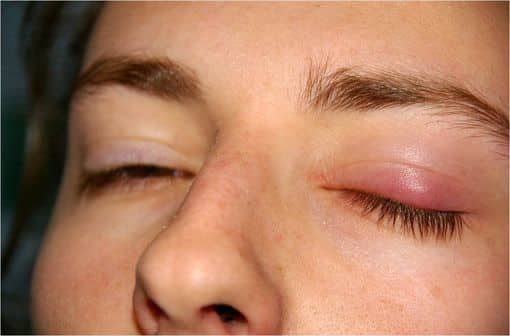
Additionally, more serious side effects may occur with prolonged use. Patients may develop a hypercorticism syndrome, characterized by clinical manifestations such as moon face, skin fragility, and osteoporosis. Special attention must be given to patients receiving long-term treatments, as sudden discontinuation of treatment may lead to withdrawal symptoms, including muscle pain and weakness.
Contraindications to the Use of Dexamethasone
It is crucial to thoroughly evaluate a patient’s medical history before prescribing dexamethasone. Given its powerful effects, certain absolute contraindications exist. Among these, we note:
- Infectious arthritis: Treatment with corticosteroids could worsen the infection.
- Periarticular calcification: This may complicate the management of joint pain.
- Viral hepatitis: Immunosuppression may worsen an existing viral infection.
- Herpes: Corticosteroids may trigger outbreaks in patients with a history of herpes.
- Hypersensitivity: Any previous reaction to dexamethasone or to sulfites present in its formulation is a contraindication.
A rigorous evaluation is essential before prescribing this medication, as potential complications can easily outweigh the benefits. Furthermore, in patients with a history of pheochromocytoma, a rare tumor of the adrenal glands, dexamethasone may trigger a potentially fatal crisis. Other precautions include the simultaneous use of medications that may lead to torsades de pointes or other cardiac complications.
In summary, prescribing dexamethasone requires special attention to both side effects and contraindications. For more in-depth information on the clinical implications of using this medication, you can consult the website Doctissimo or the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products, particularly for data on associated side effects.
FAQ on Medical Prescription of Dexamethasone
What are the side effects of dexamethasone? Dexamethasone can cause various side effects, including hyperglycemia, hypertension, weight gain, and symptoms of hypercorticism such as swelling.
What are the contraindications to the use of dexamethasone? There are several absolute contraindications, such as infectious arthritis, periarticular calcification, viral hepatitis, and herpes. Additionally, hypersensitivity to any of its components is also a reason to avoid this treatment.
What risks do repeated injections of dexamethasone pose? Repeated injections may lead to symptoms of hypercorticism and disrupt the body’s balance, which includes weight gain and other adverse effects.
Can dexamethasone cause serious complications? Yes, in the case of pheochromocytoma, a rare type of tumor, treatment can induce a pheochromocytoma crisis, which can be fatal if not treated.
How does dexamethasone interact with other medications? It is generally not recommended to use it in conjunction with non-antiarrhythmic medications, as this may lead to torsades de pointes.
What are withdrawal symptoms after prolonged treatment? Sudden discontinuation of dexamethasone can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as fever and pain.
What precautions should be taken when using this medication? It is crucial to monitor blood sugar and blood pressure during treatment, especially if the treatment is prolonged.