Cardiac health is a topic that raises many concerns, and among the frequently prescribed treatments is digoxin. This medication, derived from plants, is primarily used to treat certain heart conditions, including heart failure and rhythm disorders. However, while digoxin can offer significant therapeutic benefits, its use requires heightened vigilance due to the side effects and contraindications that accompany it. Various complications can arise, such as digestive disturbances, arrhythmias, and manifestations of bradycardia, which are signals of a potential overdose. Furthermore, certain medical conditions, such as atrioventricular blocks or renal failure, make its use inappropriate. A thorough understanding of these elements is essential to ensure the safety of patients when prescribing this medication. By exploring the adverse effects and situations that contraindicate the use of digoxin, it becomes possible to optimize treatments while minimizing associated risks.

Digoxin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat certain heart disorders, including heart failure and some arrhythmias. As a cardiotonic, it exerts a positive inotropic effect, meaning it helps strengthen the heart’s contraction. However, like any medication, digoxin has side effects and contraindications that it is crucial to know to ensure safe and effective use.
Side effects of digoxin
The use of digoxin can lead to various adverse effects, which vary depending on each patient’s sensitivity, the dosage administered, and the duration of treatment. The most common side effects include digestive disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These manifestations are often the first signs of a overdose, which can also lead to loss of appetite.
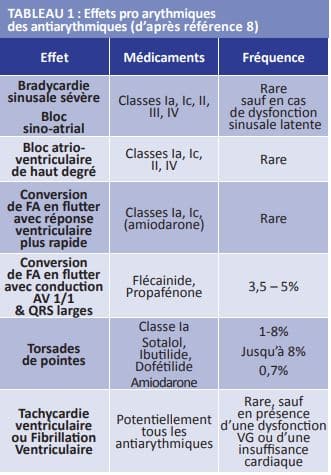
Another set of symptoms that may be observed includes conduction disturbances and cardiac excitability issues, such as bradycardia (slowing of the heart rate) and various types of arrhythmia, including supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and ventricular extrasystoles. In some cases, patients may also experience ventricular hyperexcitability, highlighting the importance of closely monitoring cardiac responses during treatment.
It is essential to remember that the side effects of digoxin can be exacerbated by external factors, such as renal failure, hypokalemia, or the simultaneous use of other medications. Patients taking digoxin should be informed of warning signs and know when to consult a physician.
Contraindications to digoxin prescription
Before prescribing digoxin, a healthcare professional must carefully assess potential contraindications. This medication should never be used in patients with an unpaced atrioventricular block of the 2nd or 3rd degree. Additionally, patients with severe cardiac conduction disorders should also be excluded from this treatment due to the high risks of arrhythmia.
Particular attention should be given to individuals with a history of digoxin overdose, as well as those with significant renal disorders. Indeed, digoxin is primarily eliminated via the kidneys, and impaired kidney function can increase the risk of accumulation of the substance in the body.
It is also advised to avoid prescribing digoxin to patients with hypomagnesemia or hypokalemia, as these electrolyte conditions can enhance the toxic effects of the medication. Thus, it should be used cautiously in elderly individuals or those with comorbidities, particularly in geriatric settings.
Monitoring and usage precautions
To ensure patient safety, regular monitoring is imperative during the administration of digoxin. Blood tests may be recommended to evaluate electrolyte levels, especially potassium and magnesium, as well as digoxin concentrations to prevent complications related to overdose.
Physicians should also consider the potential effect of foods on the absorption of digoxin. For example, foods rich in fiber may interfere with the absorption of the medication, making it crucial to discuss dietary habits with the patient. Furthermore, it is important to avoid products such as gruaud, which have shown an impact on the bioavailability of digoxin.
In conclusion, although digoxin is a powerful and effective medication for treating certain heart problems, its use must be closely monitored due to potential side effects and contraindications. This necessitates rigorous medical follow-up and open communication between the patient and the healthcare professional to optimize management and minimize risks.
FAQ on medical prescription: side effects and contraindications of digoxin
What are the possible side effects of digoxin? Commonly reported side effects include digestive disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Significant loss of appetite and visual disturbances may also occur.
What are the consequences of a digoxin overdose? In cases of overdose, patients may experience digestive disturbances, ventricular extrasystoles, as well as excessive bradycardia, resulting from increased ventricular excitability.
Who should not take digoxin? Digoxin is contraindicated in patients with unpaced atrioventricular blocks of the 2nd and 3rd degree.
What symptoms should raise concerns when taking digoxin? Symptoms to monitor include nausea, excessive weakness, and confusion, which may indicate an overdose or serious adverse effects.
What are the risks of complications with digoxin? Complications may include autonomic disorders such as bradycardia or sinus arrest, and cardiac arrhythmias that require medical attention.