Olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic widely used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Although it is effective in mood regulation due to its antipsychotic properties, this active substance can lead to notable side effects. Physicians must therefore be attentive to the contraindications to ensure patient safety while managing their disorders adequately.
The olanzapine is a medication classified among atypical antipsychotics, commonly prescribed for the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. This medication primarily works by modulating neurotransmitter systems in the brain, notably dopamine and serotonin. Although it is effective in managing certain mental disorders, it is associated with a range of side effects and contraindications that are crucial to know before initiating treatment.
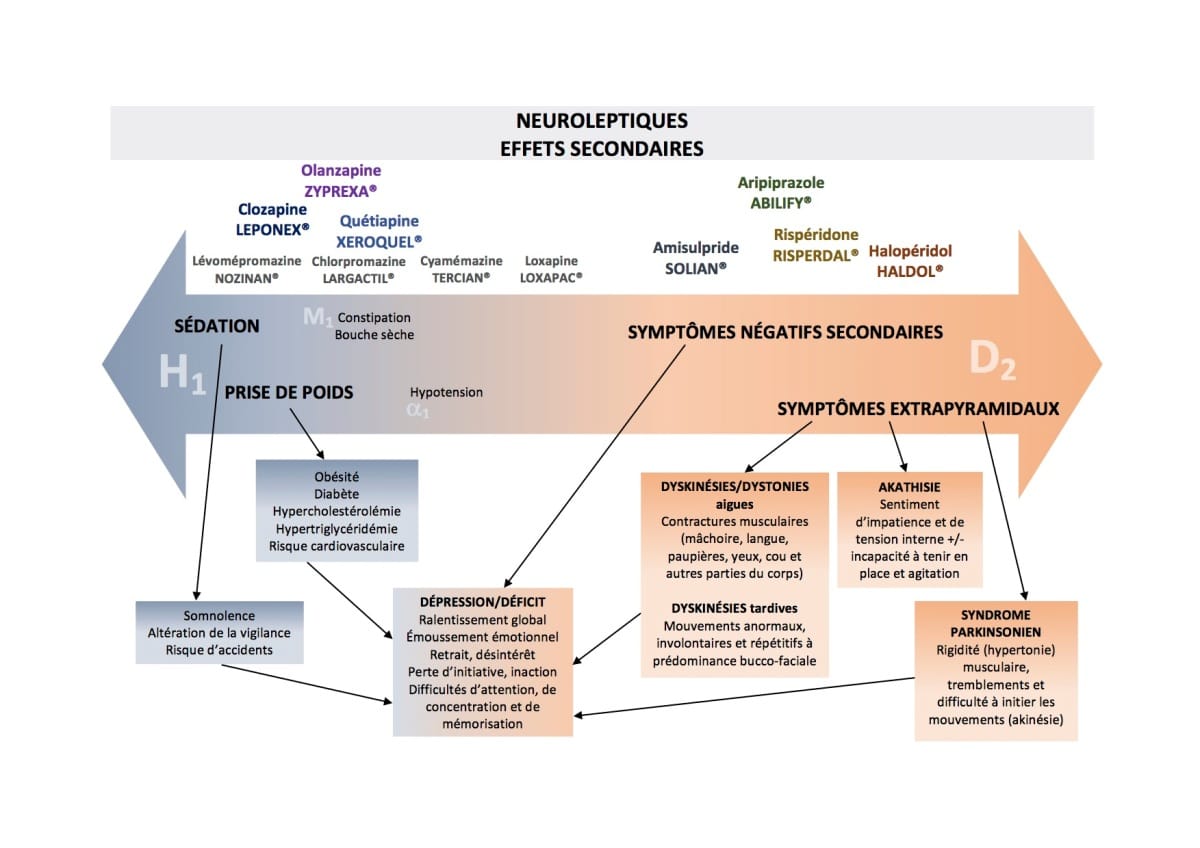
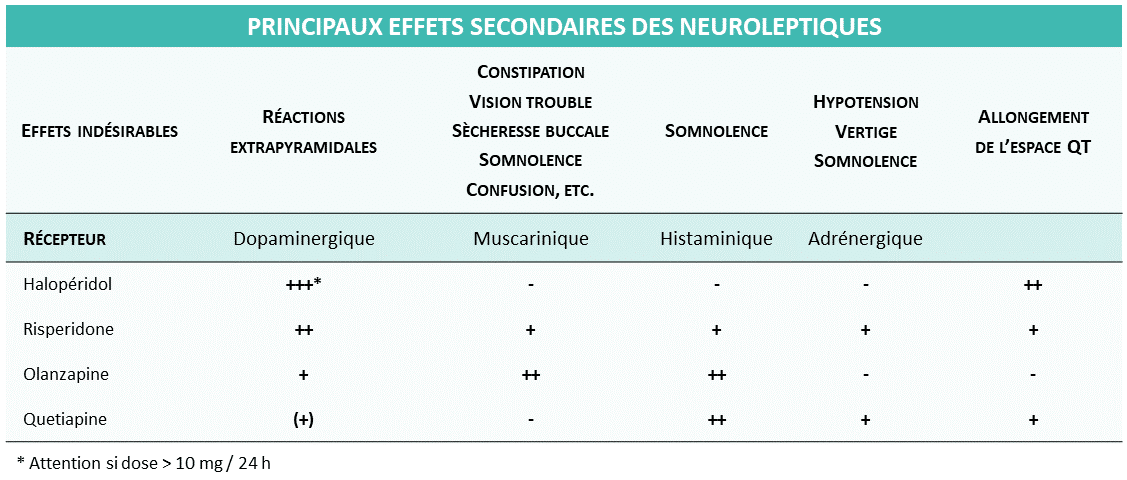
Frequent side effects of olanzapine
During treatment with olanzapine, patients may encounter various adverse effects. Among the effects reported in clinical trials, some manifest in more than one in ten patients, which necessitates increased vigilance during the treatment period.
Among the very common side effects, drowsiness is noted, which can affect the ability to perform activities requiring sustained concentration. Patients may also experience significant weight gain, often attributed to increased appetite. These changes can lead to long-term complications, such as the development of metabolic diseases, including diabetes.
Other notable side effects include dizziness, especially when the patient stands up quickly after lying down, which can lead to falls or accidents. Changes in prolactin, cholesterol, blood sugar, and triglyceride levels are also frequently observed, making regular blood tests essential to monitor the patient’s overall health during treatment.
Contraindications of olanzapine
Although olanzapine is effective, certain conditions make its use inappropriate. The first contraindication concerns individuals with hypersensitivity to this substance or to one of the components of its formulation. Indeed, allergic reactions can vary from mild to potentially severe.
The risk of closed-angle glaucoma is another contraindication, as the use of this medication could worsen this condition. Additionally, patients suffering from dementia should avoid using olanzapine, as it may pose additional health risks. Cardiac disorders, particularly those affecting heart rhythm, also constitute an important precaution, as the medication may exacerbate these conditions.
Particular attention must be given to patients who take other medications that may interact with olanzapine. Notably, some medications, such as those containing dopaminergic agents or antacids, can reduce its effectiveness or increase the risk of adverse effects. It is therefore imperative to inform the healthcare professional of all medications taken before starting treatment with olanzapine.
Monitoring and precautions during treatment with olanzapine
During treatment with olanzapine, it is essential to ensure regular monitoring of side effects. Physicians should conduct periodic assessments aimed at detecting any significant changes in the patient’s health status. Regular blood tests are recommended to monitor cholesterol, blood sugar, and other metabolic parameters to prevent complications related to weight gain or endocrine disorders that may occur.
Furthermore, educating patients about the necessity of reporting any physical or emotional changes, such as mood alterations or the appearance of unfamiliar physical symptoms, is essential for effective management of their treatment. This information allows for dose adjustments or exploration of other therapeutic options if necessary.
Patients must also be informed of potential interactions between olanzapine and certain foods, such as grapefruit juice, which can alter the metabolism of the medication and increase the risk of side effects. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid such foods during the treatment period.
In summary, olanzapine is an effective medication for treating various mental health conditions, but its use must be governed by specific precautions. The side effects and contraindications require particular attention to ensure patient safety and health throughout the therapy.

FAQ on prescription medical: side effects and contraindications of olanzapine
Q: What is olanzapine?
A: Olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorders.
Q: What are the common side effects of olanzapine?
A: The most common adverse effects may include drowsiness, weight gain, feelings of discomfort, as well as increases in cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Q: Who is olanzapine not recommended for?
A: This medication is not recommended for individuals with hypersensitivity to olanzapine, those with a risk of closed-angle glaucoma, and patients with dementia.
Q: Does olanzapine have interactions with other medications?
A: Yes, olanzapine can interact with other substances and decrease the absorption of medications taken simultaneously. It is advised to maintain an interval of at least two hours between olanzapine and other treatments such as antacids.
Q: How should the dosage of olanzapine be adjusted?
A: The dosage may vary according to the individual needs of the patient, and a therapeutic window of one week is recommended to eliminate side effects during a treatment switch.
Q: What are the very common adverse effects related to olanzapine?
A: At the beginning of treatment, individuals may experience dizziness or feelings of discomfort, particularly when transitioning to a standing position.
Q: Can olanzapine lead to dependence?
A: Olanzapine is generally not associated with a risk of dependence, but patients should follow their doctor’s recommendations to avoid adverse effects.