Recent scientific advances have allowed the emergence of new molecules intended for the treatment of bipolar disorder, bringing hope to patients suffering from this complex pathology. Among the therapies available, lithium and miscellaneous antiepileptics are often used as first intention. However, only a third of patients respond to traditional treatments, highlighting the importance of understanding molecular mechanisms underlying and to explore new therapeutic avenues. The association of these latter molecules with existing treatment protocols could potentially lead to better management of manic-depressive manifestations, making research on these treatments a crucial issue in psychiatry.
|
IN BRIEF
|
THE bipolar disorder represent a major therapeutic challenge due to the complexity of their clinical manifestation. The impact of new molecules on their treatment is crucial, particularly with advances in the understanding of the underlying biological mechanisms. In this article, we examine the importance of these new therapeutic strategies, such as the use of antiepileptic drugs and lithium, and their effect on brain physiology and clinical effectiveness.
The role of lithium and antiepileptics
THE lithium remains the standard treatment for many patients with bipolar disorder. It works by stabilizing mood and reducing the intensity and frequency of manic episodes. However, responses to lithium are varied, with complete effectiveness observed in only 30% of patients. To complete the therapeutic offer, antiepileptics such as valproic acid and lamotrigine are also prescribed, providing notable antidepressive benefits, particularly during the depressive phases of the disease.
Neurobiological effects of new molecules
Recent studies have highlighted the positive effects of lithium on neuronal structure. The treated patients present a increased dendrite density, suggesting increased neuroprotection. Additionally, valproic acid has been shown to influence the development of the nervous system, paving the way for further research into its effects at the neuronal level. These advances offer promising avenues for more targeted and effective treatments.
Combined treatment strategies
In many cases, the combined use of different medications is necessary to address the complexity of symptoms associated with bipolar disorders. THE antidepressants can be beneficial, but their use must be carefully integrated with mood stabilizers to avoid the risk of mania. Therapeutic choices are often influenced by individual reactivity to different molecules and their side effects.
Limitations and future perspectives
Despite progress, the treatment of bipolar disorder remains limited, notably the reluctance of some patients to undergo long-term treatment, mainly due to side effects potential of drugs. The importance of expanding research into the effect of new molecules and exploring alternatives means that scientists are constantly striving to better understand these disorders and improve clinical management. Ongoing research is looking at new classes of drugs that may be effective with fewer side effects.
Research continues to shed light on the impact of new molecules in the treatment of bipolar disorders. By integrating more targeted approaches and investing in advanced diagnostic tools, the hope of improving the quality of life of patients with bipolar disorders is fundamental.
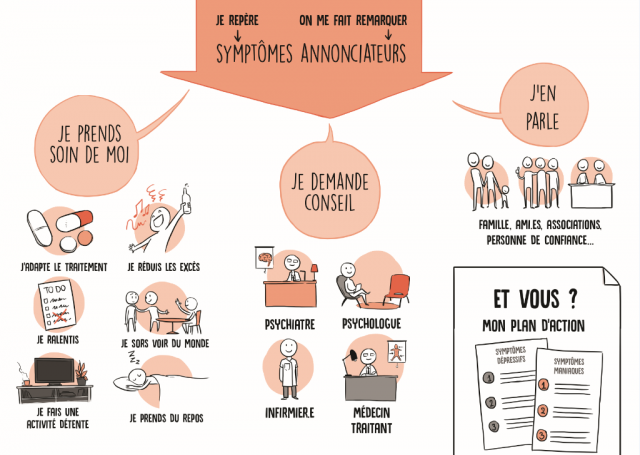
THE bipolar disorder represent a complex pathology that requires appropriate management. Recently, the emergence of new molecules has broadened the range of available treatments. Among these innovations, certain molecules show promising potential in the treatment of manic and depressive episodes. This document presents the significant advances linked to these new therapeutic options and offers recommendations for their use.
New molecules and mechanisms of action
New molecules developed for the treatment of bipolar disorder include medicines from different classes, including antidepressants, of the antipsychotics atypical and antiepileptics. Each of these substances acts on different neurobiological axes, thus influencing the underlying mechanisms of the disease. For example, molecules likevalproic acid and the lithium involved in the modulation of neurotransmitters and the regulation of intracellular signaling pathways. It is essential to understand these mechanisms to optimize therapeutic choices.
Use of lithium in treatment
THE lithium remains a reference treatment for bipolar disorder. Its effectiveness is indisputable, but it is also crucial to consider its potential side effects and its long-term impact on patients’ health. Recent studies have shown that the lithium could have a positive effect on the density of dendrites in certain regions of the brain, suggesting real neuronal reconstruction in treated patients. However, its individual tolerance requires particular attention, emphasizing the importance of regular clinical monitoring.
Antidepressants and mood stabilizers
THE antidepressants can be used in combination with mood stabilizers to treat the depressive phases of bipolar disorders. However, their use must be done with caution, as there are significant risks of mania may occur. New analyzes tend to show that certain antidepressants, when used in conjunction with stabilizers like lithium or thevalproic acid, can significantly improve depressive symptoms while minimizing risks. This highlights the need for tailor-made treatment based on the clinical course of each patient.
Benefits of antiepileptics
THE antiepileptics, such as the lamotrigine and the carbamazepine, are also very useful in the treatment of bipolar disorders, particularly for the management of manic episodes. Their ability to stabilize mood and reduce the frequency of relapses has made them valuable allies in the management of these disorders. In addition, the search for repositioning of certain molecules demonstrates the imperative to expand our therapeutic arsenal, because only 30% of patients respond fully to lithium alone.
Conclusion and practical recommendations
It is therefore recommended that practitioners keep in mind the diversity of new molecules and their mechanisms of action when treating patients suffering from bipolar disorders. Regular and personalized monitoring is essential to adapt the treatment and minimize the risk of side effects. Involving patients in therapeutic choices, as well as continuing training for healthcare professionals, will contribute to better management of bipolar disorders on a daily basis.
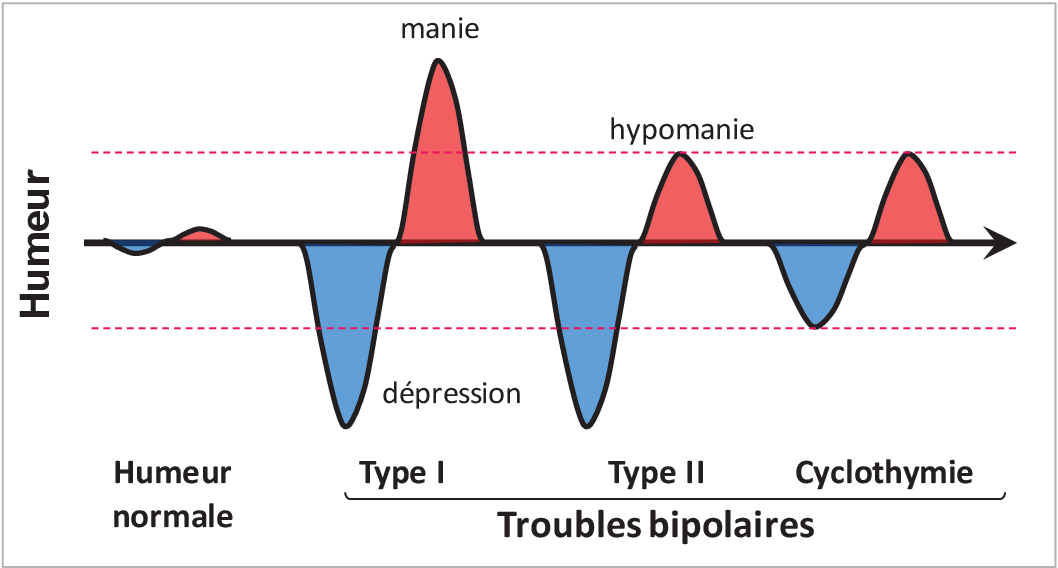
THE bipolar disorder represent a set of complex mental illnesses that profoundly impact patients’ quality of life. The constant search for new therapeutic molecules has led to significant advances in the treatment of these conditions. Compounds such as lithium and thevalproic acid have long been cornerstones in the management of manic and depressive episodes. However, new avenues are being explored to overcome the limitations of current treatments.
Recent discoveries in the area of molecular mechanisms offer promising insight into the pathophysiological processes underlying bipolar disorder. For example, studies have found that lithium not only stabilizes mood, but also increases dendrite dependence in the brain, which could promote neuronal plasticity. These beneficial effects highlight the importance of continuing to expand our understanding of the neurobiological pathways influenced by these drugs.
Additionally, the exploration of new drugs, such as antidepressants and others mood stabilizers, makes it possible to treat more refractory forms of bipolar disorders. Combining these therapies with first-line medications like lithium could optimize outcomes for many patients. However, the management of side effects, which can be problematic for certain treatments, remains a major challenge.
Finally, research must continue to focus on repositioning of molecules already existing and the identification of new therapeutic targets to improve the effectiveness of treatments and reduce drug resistance. Advances in this area are essential for developing more personalized treatment protocols, tailored to the specific needs of each patient suffering from bipolar disorder.