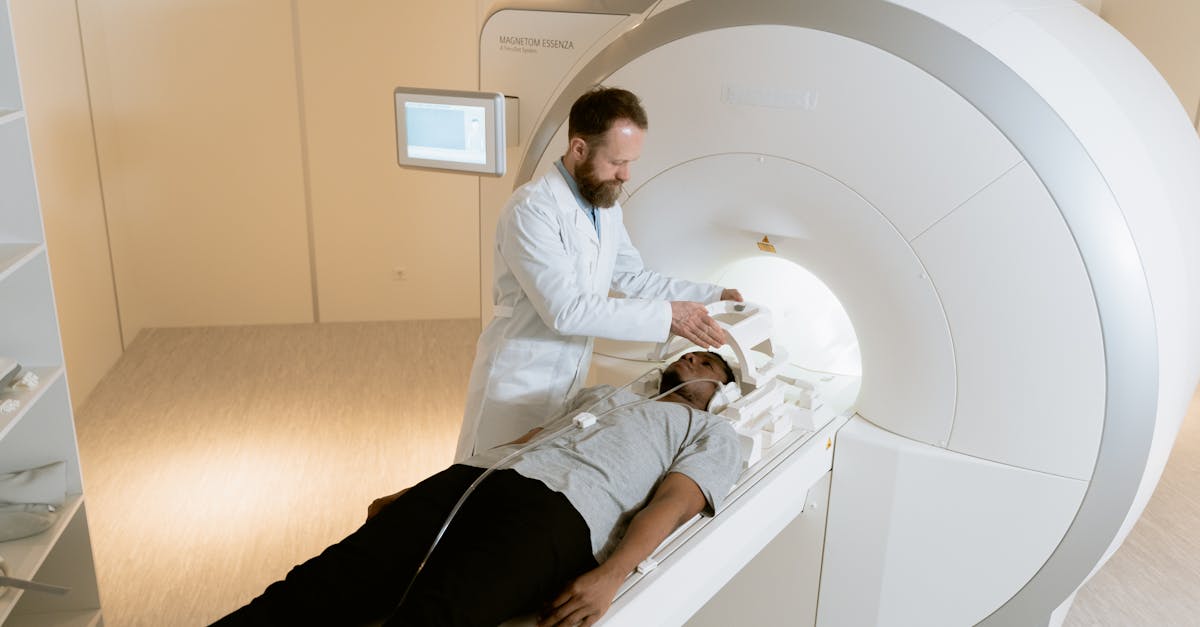
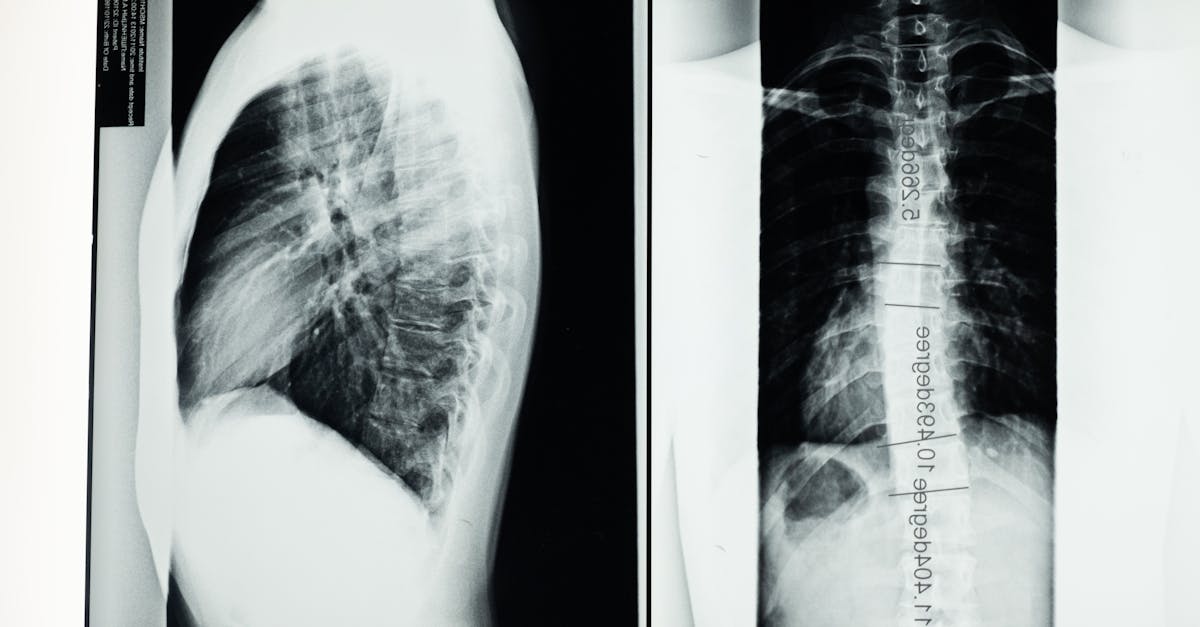
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has experienced technological revolutions which open up new perspectives for medical diagnosis. Thanks to equipment such asMRI Isolde, offering an unprecedented magnetic field, it is now possible to obtain images of the brain with unequaled precision. These advances facilitate the early identification of harmful pathologies, such as neurodegenerative diseases and theepilepsy. The evolution of MRI systems, coupled with the optimization of examination protocols, not only improves image quality but also reduces acquisition time, thus strengthening the capacity to provide faster and more accurate diagnoses. reliable.
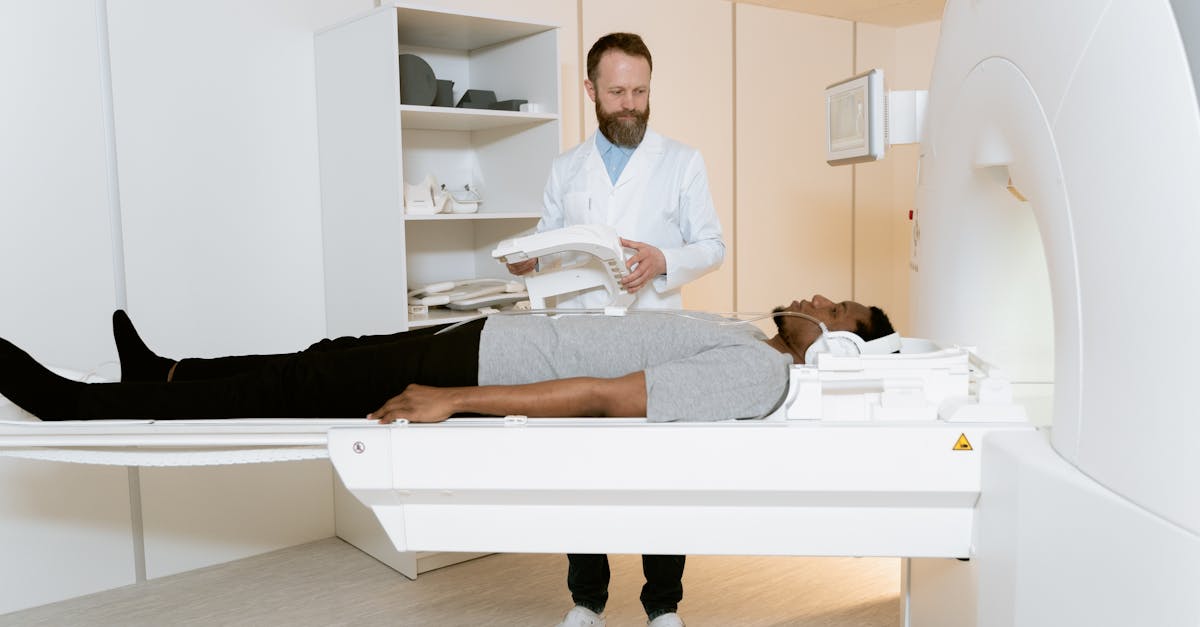
L’magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cutting-edge technology that has revolutionized the field of medicine by enabling non-invasive imaging of the internal structures of the human body. Since its introduction into the medical field, MRI has undergone several significant technical developments, resulting in a continuous improvement in image quality, the speed of execution of examinations, and patient safety. These recent advances demonstrate ongoing innovation in this field, promising new possibilities for diagnosis and medical monitoring.
In 2021, the CEA (Atomic Energy and Alternative Energies Commission) revealed for the first time a series of brain images obtained using the MRI scanner Isolde. This device, equipped with a particularly powerful magnetic field, made it possible to visualize the brain in a new way, with unprecedented precision. This type of MRI is distinguished by its ability to obtain images with micrometer resolution, thus opening the way to a level of detail previously inaccessible in the analysis of brain tissue.
The progress made in theMRI have also been the result of continuous technological evolution, including developments in the design ofmagnets high performance and optimized image sequences. Currently, systems like the MRI range SIGNA™ 1.5T are designed not only to improve exam efficiency and productivity, but also to maximize diagnostic potential through more accurate image interpretation. These emerging technologies have a direct impact on diagnostics, particularly in the context of complex diseases such as cancers or the neurodegenerative diseases.
Image quality is one of the crucial aspects that has benefited from recent advances. The optimization of MRI equipment has made it possible to increase the magnetic field, a determining factor for the clarification of the images obtained. High magnetic field systems, compared to conventional MRIs, provide much more detailed images, thus allowing a more precise assessment of pathologies. These improvements are essential for the detection and early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases and other critical medical conditions.
Advances inmagnetic resonance imaging are also accentuated by the development of innovative imaging protocols which allow specific tissues to be explored in a more targeted manner. This is particularly useful in advanced diagnostics where the need for a detailed analysis of structures is essential, as in the case ofepilepsy. Research on the advanced diagnostics and emerging treatments in this area show how MRI can contribute to better understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms of this condition and to monitoring the evolution of treatments.
Another key aspect of recent progress is the reduction of exam time. Thanks to the application of new imaging techniques, it is now possible to obtain results more quickly, which is beneficial both for patients, often in a state of stress or discomfort during examinations, and for medical staff who can perform more tests in a day. Imaging methods such as magnetoencephalography (MEG) and functional MRI (fMRI) make it possible to explore brain activity in real time, providing additional information during clinical assessments.
The integration of technologies is another major breakthrough. The use of AI in MRI image processing and clinical decision-making enables faster and more accurate data analysis. Machine learning algorithms can detect aberrations or abnormal structures in images, facilitating early diagnosis, as discussed in studies investigating early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. This technology promises to refine results and confirm or deny diagnoses faster than before.
Recent developments in MRI go beyond brain imaging and also affect other medical fields, such as cardiology and oncology. For example, in the context of oncology, MRI is used to monitor the response of a tumor to treatment, thus making it possible to adapt therapeutic protocols according to the results obtained. This highlights the importance of MRI not only for initial diagnosis, but also for longitudinal follow-up of affected patients.
There are also advances invery low field magnetic resonance imaging which refer to a new approach to medical imaging. This type of system, which focuses on acquiring high-quality images at lower magnetic fields, has the advantage of reducing exposure to strong magnetic fields for patients while maintaining excellent image resolution .
Despite all these encouraging developments, it is important to note that progress in magnetic resonance imaging are not without challenges. Radiologists and other healthcare professionals must constantly adapt their practices to these new technologies, which requires ongoing training and appropriate clinical equipment. In addition, there remain limitations and ethical considerations, particularly in terms of cost and accessibility to these technological advances for the entire population.
In summary, themagnetic resonance imaging continues to evolve at a rapid pace, providing fascinating possibilities for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. With exceptional technological advances, modern MRI systems are now capable of producing images of unparalleled quality that lead to a more precise understanding of pathologies. Continued exploration of this path promises to transform the landscape of modern medicine, increasing the ability of healthcare professionals to provide precise, tailored care to patients.

Recent advances in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) marked a significant turning point in the medical field, offering high-precision diagnostic tools. Thanks to new technologies and constant innovation, MRI now makes it possible to obtain brain images of unprecedented resolution and improve the diagnosis of neurological diseases. This article presents the latest technical developments inMRI, the benefits they provide and the implications for patient monitoring.
Cutting-edge MRI technology
The systems ofMRI new generation, such as the Iseult MRI, are distinguished by their exceptionally powerful magnetic field, of up to 7 Tesla. This technological development makes it possible to obtain a micrometric resolution brain tissue, making previously indistinguishable structures visible. These advances are essential for the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases and for pathologies such as epilepsy, where fine imaging is crucial.
Improved image quality
Recent innovations in imaging techniques have improved the quality of the images produced by theMRI. Increasing the magnetic field helped reduce artifacts and maximize visual clarity, resulting in more reliable diagnostics. High-field MRI systems, such as those in the SIGNA™ family, are designed to maximize diagnostic productivity, thereby increasing exam efficiency and facilitating patient care.
Advanced clinical applications
The new capabilities ofMRI play a crucial role in the diagnosis of cancers, allowing better localization and precise assessment of the extent of lesions. Doctors can now leverage these advanced diagnostics to create more personalized treatment plans. Additionally, MRI helps monitor disease progression, which is essential for monitoring treatments and managing potential complications.
Impact on medical research
Advances in the field ofMRI are not limited to clinical practice; they also open new avenues in medical research. The precise visualization of brain structures allows researchers to better understand how the brain functions, study disease mechanisms and explore new therapies. The progress in magnetic resonance imaging thus promote more in-depth studies on complex neurological conditions and psychiatric disorders.
Ethical considerations and limitations
Despite these advances, the use ofMRI is not without challenges. The high costs associated with this new equipment and techniques may limit their accessibility in certain healthcare establishments. Furthermore, it is essential to take into account the ethical considerations related to the manipulation of imaging data, particularly with regard to the protection of patient privacy. Such issues must be carefully evaluated to ensure responsible medical practice.