Technological innovation has profoundly transformed the field of digestive endoscopy, offering new horizons for the diagnosis of digestive diseases. The latest endoscopic techniques allow more precise exploration with advanced tools, facilitating the identification of pathologies. Devices such as theultrasound endoscopy and the integration ofartificial intelligence revolutionize not only the methods of analysis, but also the treatment of conditions, notably hypertonia of the lower esophageal sphincter. This development is based on secure procedures and modern equipment, thus ensuring reliable and rapid diagnostics. Biopsy techniques, for example, are improving to ensure better tissue evaluation, reinforcing the crucial importance of endoscopy in the management of digestive disorders.
|
IN BRIEF
|
Recent advances in the field of digestive endoscopy have revolutionized the diagnosis of digestive diseases. These innovative techniques allow in-depth and precise exploration, thus contributing to better management of pathologies. This article discusses the different current methods as well as their impact on the early detection of digestive diseases.
Upper digestive endoscopy: a targeted exploration
L’upper digestive endoscopy represents a key technique in the diagnosis of conditions of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. This procedure, often carried out under sedation, allows not only to study the mucous membranes but also to take biopsies for histological analyses. Thanks to modern equipment, image quality has improved significantly, making it easier to detect abnormalities such as polyps or inflammation.
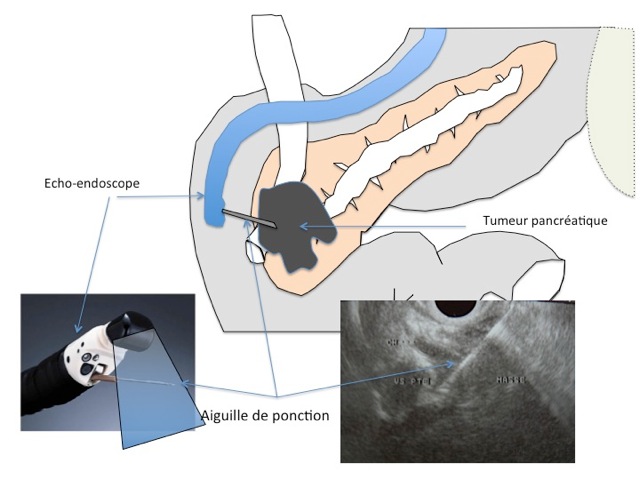
Echo-endoscopy: a fusion of ultrasound and endoscopy
L’ultrasound endoscopy has established itself as an essential complementary technique, offering a detailed view of the layers of the digestive walls. This examination combines the advantages of endoscopy and ultrasound, allowing precise assessment of masses and surrounding lymph nodes. It is particularly useful in the staging of gastrointestinal cancers and the detection of lesions undetectable by other methods.
Artificial intelligence: diagnostic support
The integration of theartificial intelligence in the field of digestive endoscopy sheds new light on image analysis. Machine learning algorithms can process thousands of images to perceive patterns and abnormalities, thereby increasing diagnostic accuracy. This promising approach could revolutionize the way doctors examine endoscopic results and guide their treatment choices.
Targeted biopsies: precision and updated protocols
THE biopsies carried out during digestive endoscopy are now guided by precise protocols. For example, it is recommended to take a minimum of four biopsies every ten centimeters of the colon, without spotting stains, to ensure adequate coverage. These precautions are essential for a reliable diagnosis, particularly in the context of detecting digestive cancers. More details can be viewed in the guide to good practices on biopsies in digestive endoscopy.
Hail exploration: emerging techniques
THE morphological explorations of the small intestine have gained importance, particularly in the diagnosis of obscure digestive bleeding. Tiny endoscopy techniques, such as capsule endoscopic, allow complete visualization of the small intestine without requiring invasive surgery. This type of approach is essential to identify the causes of bleeding, inflammation and various lesions.
State-of-the-art equipment
THE digestive endoscopy centers, like that of Saint-Antoine hospital, are equipped with advanced technologies offering a modern technical platform. These installations ensure both highly precise exploration quality and optimal safety for patients. Implementing rigorous disinfection protocols for endoscopes increases patient confidence in these procedures.
For additional information on the progress of theupper digestive endoscopy, you can consult the dedicated page on Ameli.fr.
Technological advances in the field of endoscopy have significantly improved the diagnosis of digestive diseases. THE latest endoscopic techniques not only allow in-depth exploration of organs, but also the treatment of various pathologies. This article presents the main innovations in digestive endoscopy and their impact on the diagnosis and treatment of digestive diseases.
Exploration and diagnosis by endoscopy
L’digestive endoscopy allows exploration of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, as well as the small intestine and colon. Among the most recent techniques, gastroscopy and the colonoscopy stand out for their effectiveness in detecting abnormalities such as polyps, ulcers or signs of cancer. The use of high definition cameras improves the visualization of lesions, making the diagnosis more precise.
Endoscopy-guided biopsies
Biopsies are a key part of the diagnosis. Thanks to technological advances, it is now recommended to take four biopsies minimum every 10 cm of the colon during a colonoscopy. This protocol maximizes the chances of detecting early lesions. Biopsies are quickly analyzed by pathology, providing an immediate assessment of the patient’s condition.
Advanced imaging techniques
The combination of endoscopy with techniques of, like endoscopy, allows a morphological evaluation of the digestive system. This method uses ultrasound to produce images in real time, making it easier to diagnose deep lesions. Ultrasound endoscopy is particularly indicated for the evaluation of tumors and biliary pathologies.
Artificial intelligence in endoscopy
With the emergence ofartificial intelligence, image analysis tools become valuable allies for doctors. AI makes it possible to analyze thousands of images in moments, improving anomaly detection. This progress transforms endoscopy into an even more reliable and rapid diagnostic tool. Machine learning algorithms also help standardize practices and reduce misinterpretations.
Endoscopic treatment of digestive diseases
Advances in endoscopy are not limited to diagnosis. Innovative techniques also make it possible to treat certain pathologies in a less invasive manner. For example, the treatment ofhypertonia of the lower esophageal sphincter can be achieved through an endoscopic intervention, consisting of cutting the hypertonic muscle. This method offers an interesting alternative to traditional surgery.
THE latest endoscopic techniques represent a major advance in the diagnosis and treatment of digestive diseases. Thanks to in-depth exploration methods, advanced imaging systems and the introduction of artificial intelligence, practitioners have powerful tools to improve patient care. Continuing research and innovation in this area promises to continue transforming gastroenterology.

Recent advances in the field ofdigestive endoscopy have transformed diagnostic practices for digestive diseases, offering more precise and less invasive methods. Among these innovations, we can cite the emergence of gastroscopy and the fibroscopy, which allow real-time visualization of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. These techniques, coupled with tools for innovative treatments, facilitate the early detection of pathologies such as cancers or ulcers, thus improving healing rates.
At the same time, the introduction of targeted biopsy during endoscopy marked a major turning point. Currently, it is recommended to take a minimum number of biopsies, ensuring detailed histological analysis is crucial for establishing an accurate diagnosis. Studies suggest that at least four biopsies should be taken every ten centimeters to maximize the chance of detecting tissue abnormalities.
The integration of theartificial intelligence in this area constitutes another significant advance. AI algorithms are now capable of analyzing thousands of endoscopic images with unparalleled speed and precision, enabling faster identification of lesions and better stratification of patients at risk. Endoscopy services, like those at Saint-Antoine hospital, are now equipped with advanced disinfection and traceability technologies, guaranteeing patient safety while allowing advanced morphological explorations of the hail and other sections of the digestive system.
These developments in endoscopic techniques, combined with continued training of practitioners, promise to revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of digestive diseases, offering patients increasingly adapted and secure solutions.